SNOMED CT terms are not indexed by Google! So the only way to interact with it is to index it yourself or use the SNOMED CT Browser. Let’s have a look at what this tool has to offer and explore the different features of SNOMED CT using the browser.
You can use SNOMED CT Browser hosted by SNOMED International to follow along.
Follow along with the video, or read on!
Components
Let’s start from the basics. SNOMED CT consists of multiple components. All of them together make a complex web of clinical concepts and relationships that can be used to drive intelligent clinical applications.
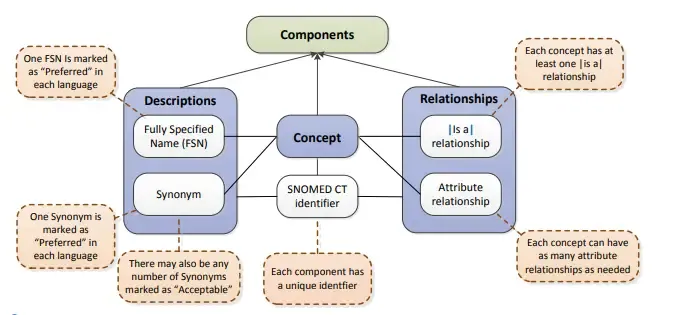
Concepts
A SNOMED CT concept is a clinical idea to which a unique concept identifier is assigned and is used to represent clinical meanings. The concepts are related to one another by relationships that provide a formal logical definition of the concept.
Descriptions
Two sorts of descriptions are used to address each idea – Fully Specified Name (FSN) and Synonym.
Synonyms: A synonym represents a term that can be used to display or select a concept. A concept may have several synonyms. This allows users of SNOMED CT to use the terms they prefer to refer to a specific clinical meaning.
Fully Specified Name: The FSN represents a unique, unambiguous description of a concept’s meaning. This is particularly useful when different concepts are referred to by the same commonly used word or phrase. Each concept can have only one FSN in each language or dialect.
Relationships
A relationship represents an association between two concepts. Relationships are used to logically define the meaning of a concept in a way that can be processed by a computer. A third concept called a relationship type (or attribute), is used to represent the meaning of the association between the source and destination concepts. Note that these relationship types are in fact, SNOMED CT concepts themselves.
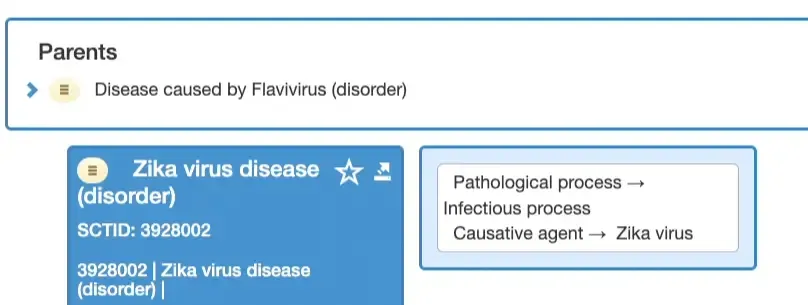
Some concepts might have multiple parents. This may seem bizarre at first, but this is part of how SNOMED CT works.
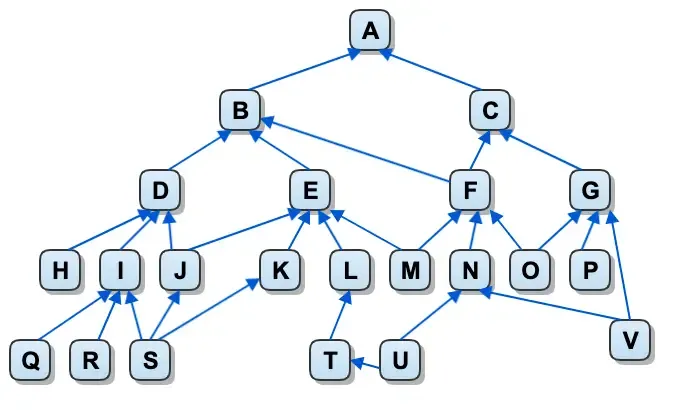
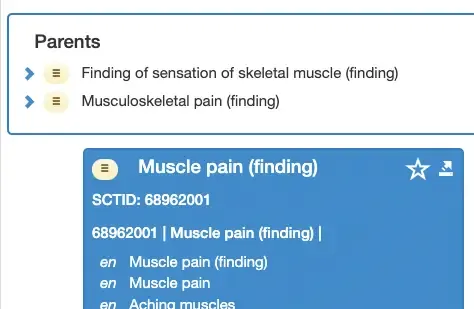 This is because SNOMED CT is a poly-hierarchy, and a concept can have multiple parents or children.
This is because SNOMED CT is a poly-hierarchy, and a concept can have multiple parents or children.
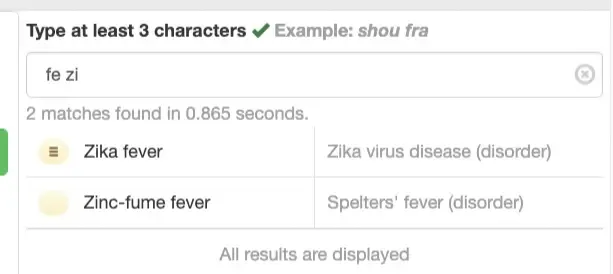
Searching
You can search terms with the starting letters: Eg: shou fra will give you “Shoulder fracture” and so will fra sho since the order doesn’t matter.
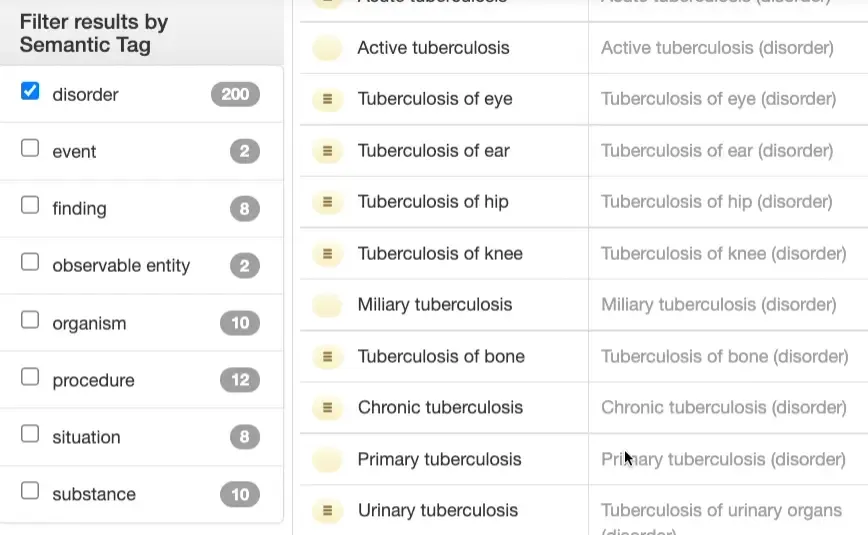
Filtering by Semantic Tags
A semantic tag indicates the top-level hierarchy to which the concept belongs. It is available from FSN (Fully Specified Name) which is the official name of the concept and is always enclosed within parenthesis. Eg: “Zika virus disease (disorder)” has a semantic tag of “disorder”.
You can easily filter based on a semantic tag by using the left panel like so:
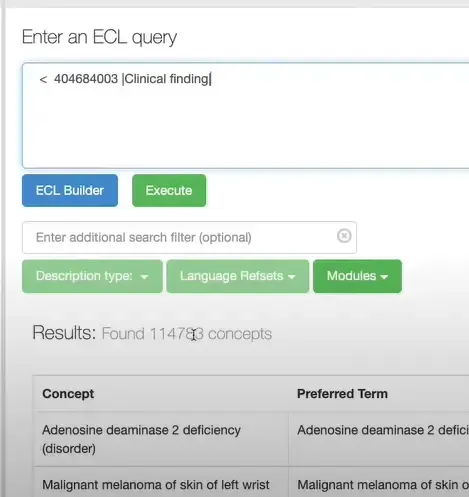
Expression Constraint Language (ECL)
Expression Constraint Language or ECL is another powerful way to search SNOMED CT.
The SNOMED CT Expression Constraint Language is a formal language for defining clinical concepts contained in pre-coordinated or post-coordinated expressions.
 You can find really good examples of how to use ECL (used throughout the video) from here.
You can find really good examples of how to use ECL (used throughout the video) from here.
Note: The expanded version of ECL eg:
descendantOf 404684003 |Clinical finding|does not work in the SNOMED CT Browser. Only the short version< 404684003 |Clinical finding|works, as of the writing of this article.
Machine Readable Concept Model (MRCM)
The Machine Readable Concept Model (MRCM) represents rules contained in the SNOMED CT concept model in a form that can be interpreted by a computer and used to confirm that concept definitions and expressions follow the rules.
In addition to the authoring and validation of SNOMED CT concepts, expressions, expression constraints, and queries, MRCM can also support Natural Language Processing and terminology binding for semantic interoperability.
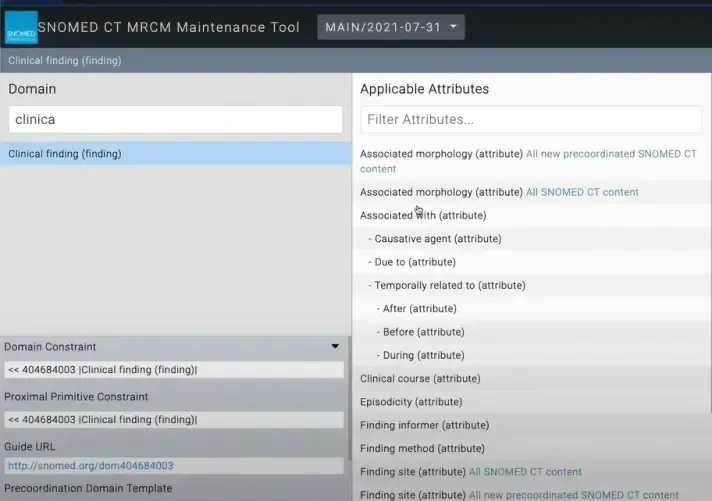 This can be used to find which types of relationships a concept can possibly have. This comes in very handy when constructing ECL queries or when creating post-coordinated expressions.
This can be used to find which types of relationships a concept can possibly have. This comes in very handy when constructing ECL queries or when creating post-coordinated expressions.
