Why do we need ERPs in Healthcare?
Medblocks is primarily focused on providing the best clinical workflow experiences to doctors and other healthcare practitioners. We also pride ourselves in capturing and storing data that comply with world-recognized standards like FHIR and openEHR.
However, a fully functioning hospital or clinic chain’s requirements are not limited to this. They also require employee and patient management, appointment scheduling, sales, purchase, inventory and billing tools, insurance integration, customer relations management (CRM), etc. While some features like patient management and appointment scheduling, are easy to implement, others require significant development effort.
We initially tended to such clients with an in-house solution or used another vendor to cater to these needs. It was simply a matter of integrating with their platform using RESTful APIs or change data capture (CDC) tools like Kafka. However, we were missing out on business opportunities with clients who wanted a single solution for their healthcare enterprise. They preferred vendors that provide all-in-one solutions, even at the expense of optimized clinical workflows.
We concluded that in-house development of these features is unproductive, as there are many Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software solutions available in the market and a tight, end-to-end integration with one of them is the best way forward. We were assisted in this integration process with ERPNext by Atul-Kuruvilla Abraham, the founder and CEO of Tacten.co.
ERPNext as an ERP solution for healthcare
ERPNext is an open-source ERP solution built using the Frappe framework. Frappe is a low-code framework written using a combination of Python and JavaScript. It comes with all the built-in components needed to develop a full-fledged software application with minimal developer effort. The Frappe community maintains and updates apps as plugins for all your enterprise needs. It also has a dedicated healthcare module that covers most of a hospital’s standard operating procedures (SOPs). Being an open-source solution, we can modify and distribute the product without incurring significant costs to clients, such as licensing fees.
In this blog, we’ll first explore a demo of ERPNext Healthcare well integrated with a health data platform like Medblocks looks like.
Then we’ll dive into the details about how to deploy the same in production on Kubernetes.
Exploring the ERPNext Healthcare Module
A full demo with explanation by Atul
Create a patient and practitioner in ERPNext
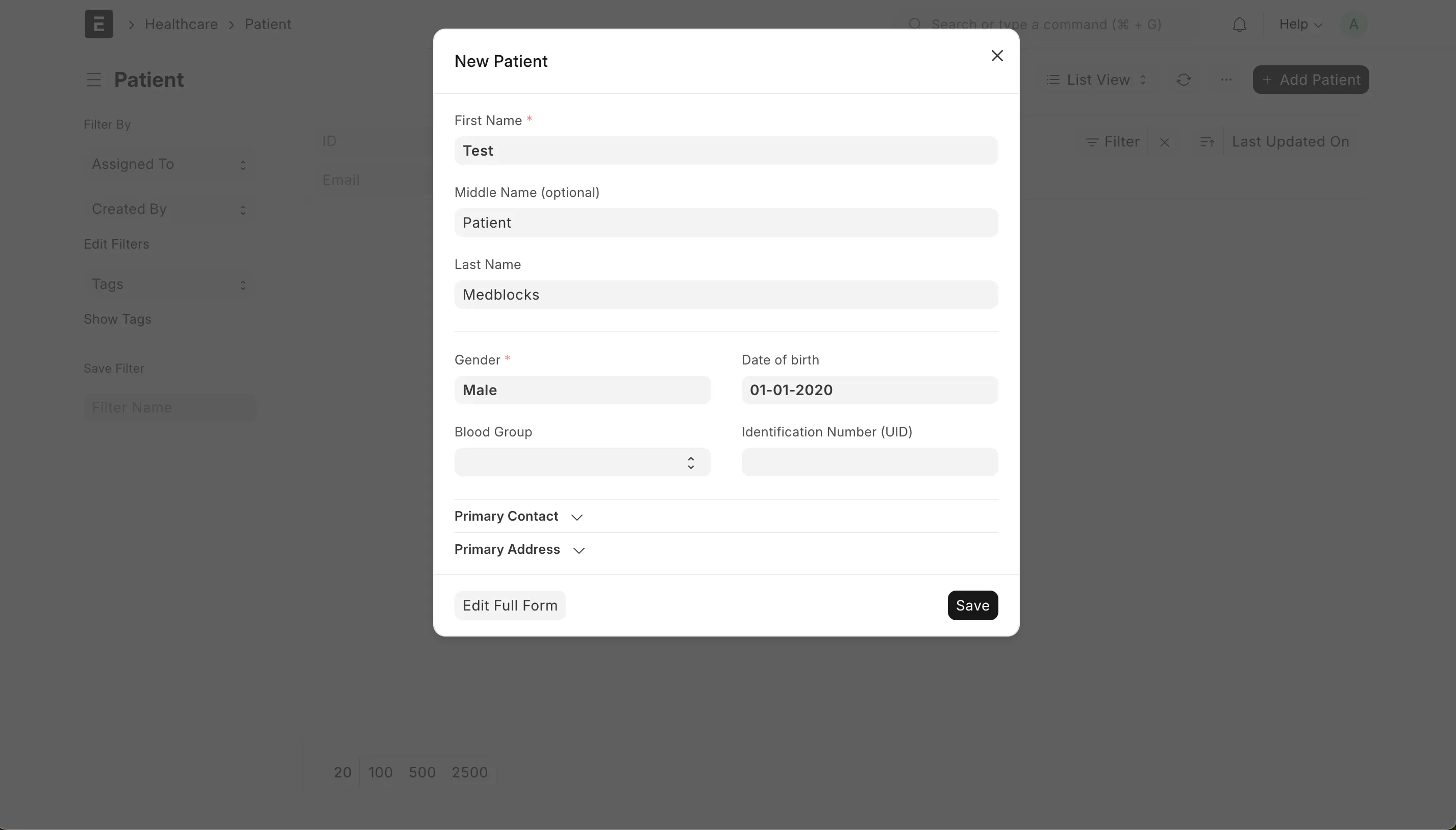
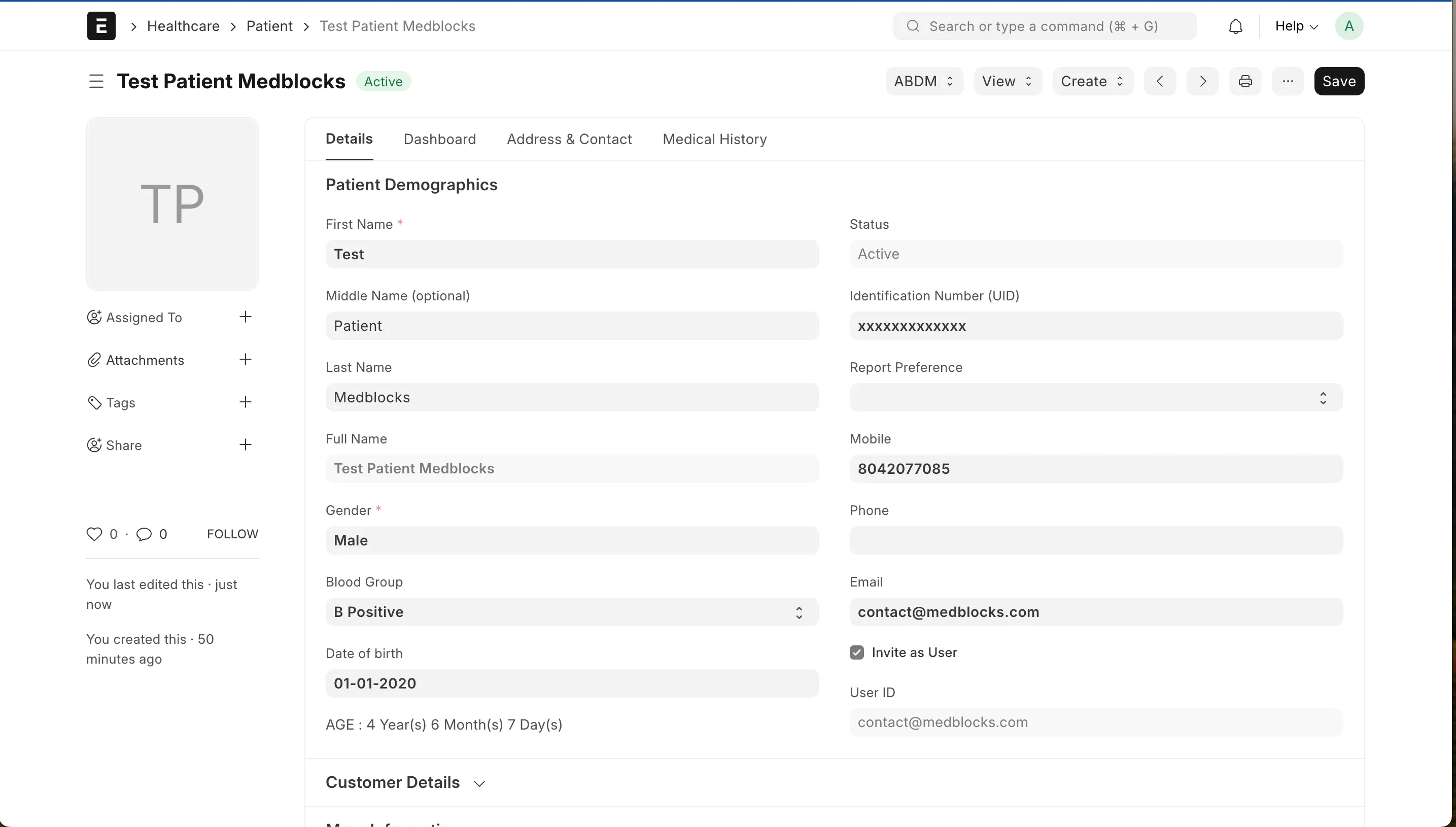
Go to Patient doctype by either going inside Healthcare module in the side bar or searching patient in search bar at the top. In search bar you will have two options, either you can directly choose New Patient or go to Patient list and click on Add Patient button. Fill the details in the popup and save. More details, if available, can be filled by clicking Edit Full Form or by going inside the patient for the Patient list view after saving.
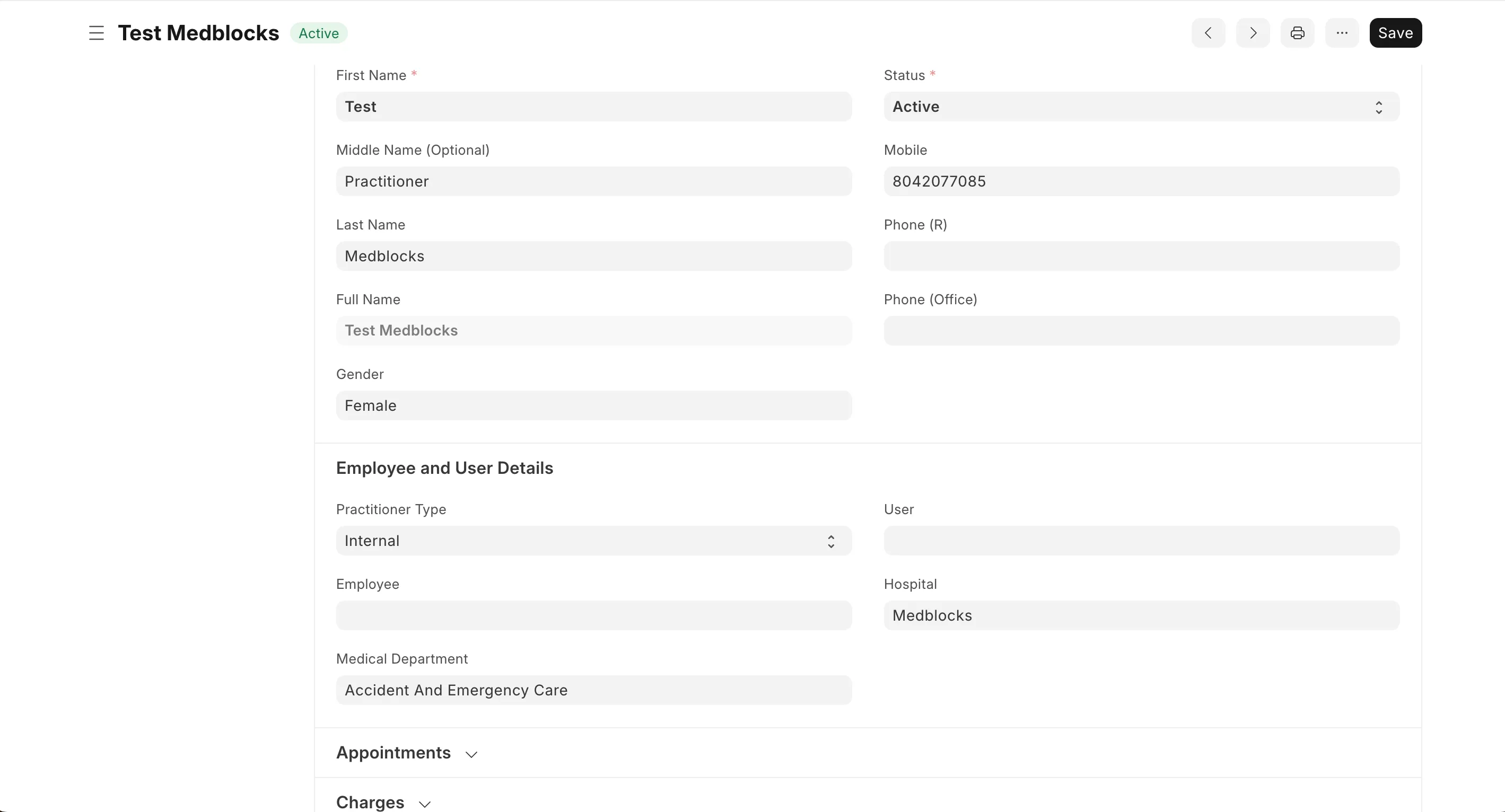
Another necessary docType to be created is Healthcare Practitioner.
Having both patient and practitioner let’s create an encounter for the patient with this practitioner.
Create an Encounter for the Patient
Some versions of Healthcare module also supports Healthcare Service Unit, associated but not to be confused with Medical Department. For the current scope we won’t be discussing Practitioner scheduling and appointments. The encounter can be created in Patient Encounter docType and saved.
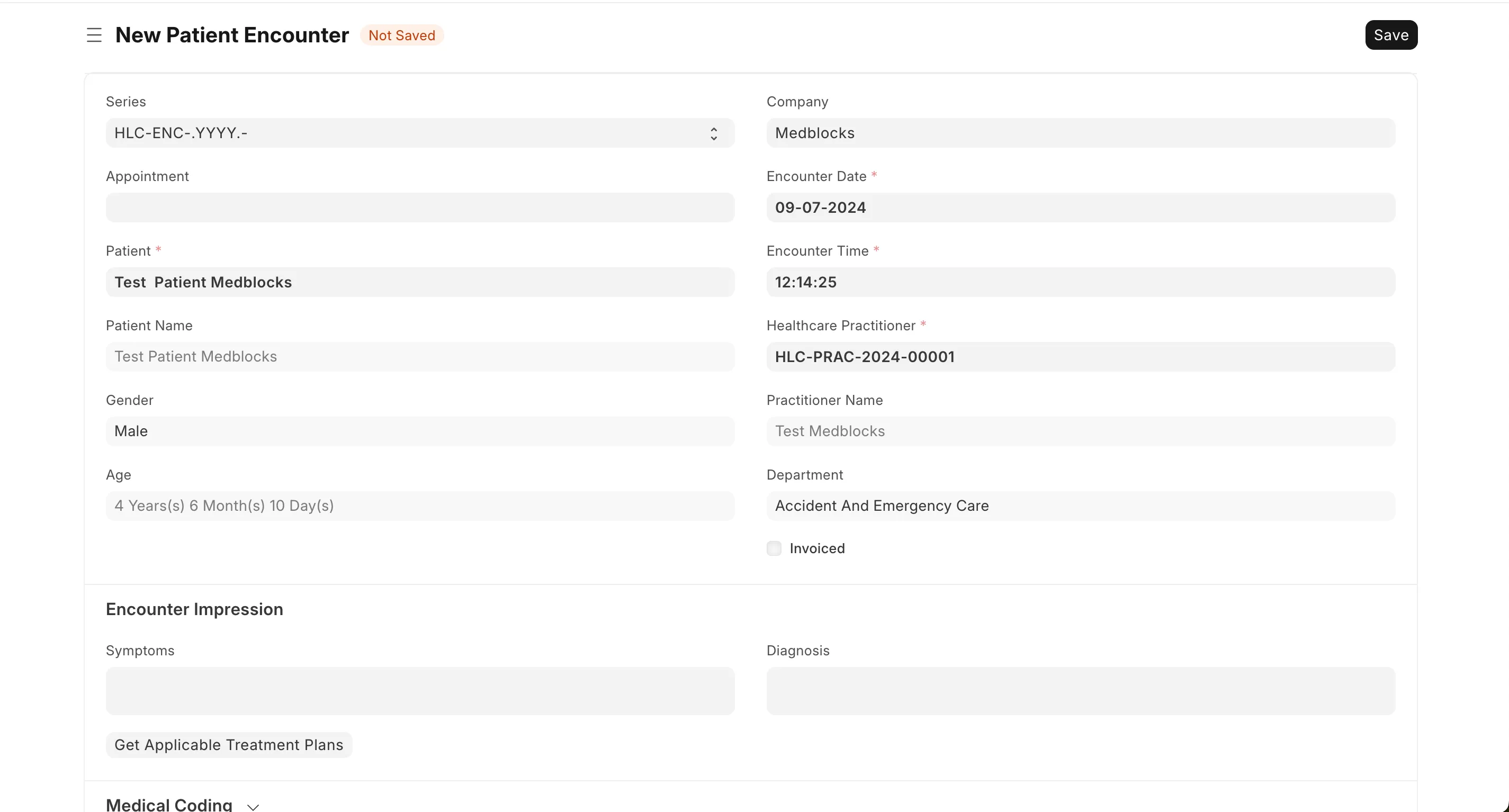
You can also create a Vital Signs document for the encounter.
Note: If using a data platform like Medblocks, you’ll want to ideally map this data entered in ERPNext to relevant openEHR archetypes and FHIR resources.
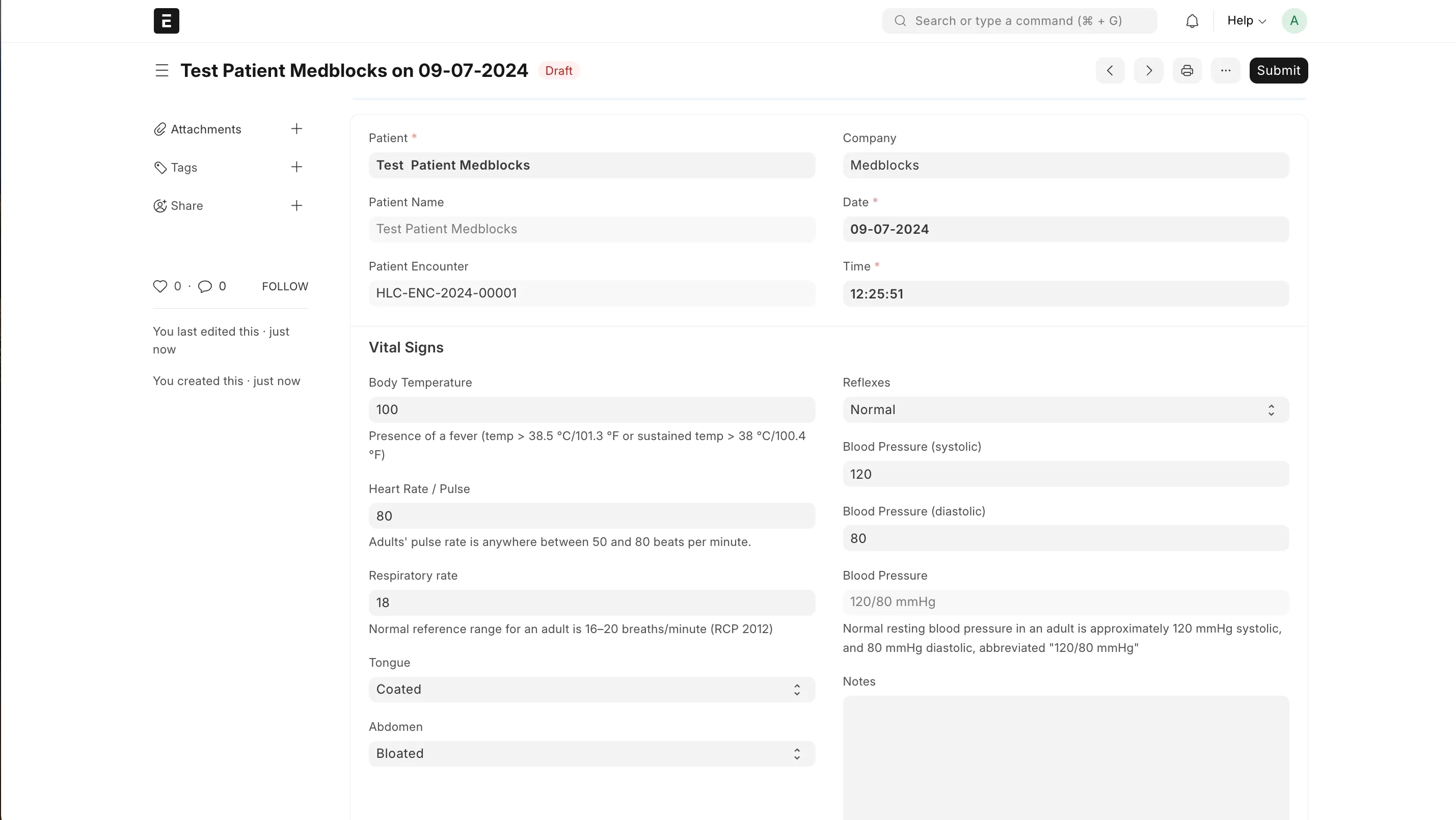
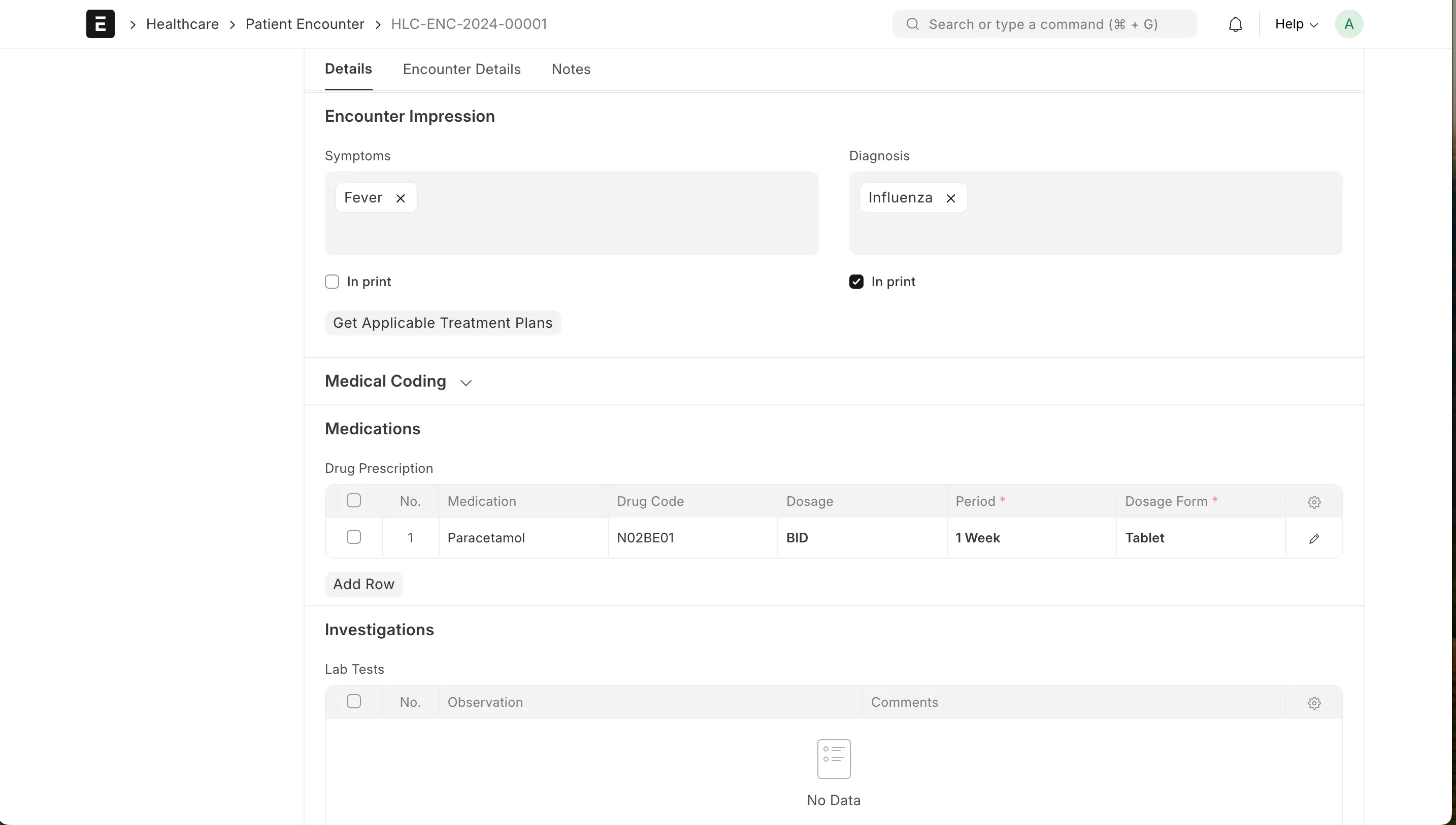
The Encounter also has fields to record symptoms and diagnosis. These can be selected from a dropdown and a new one can be created easily from the same page if necessary.
Prescribing medications and lab tests
We will then add a medication, paracetamol, for a week. Create a new one in Medication docType.
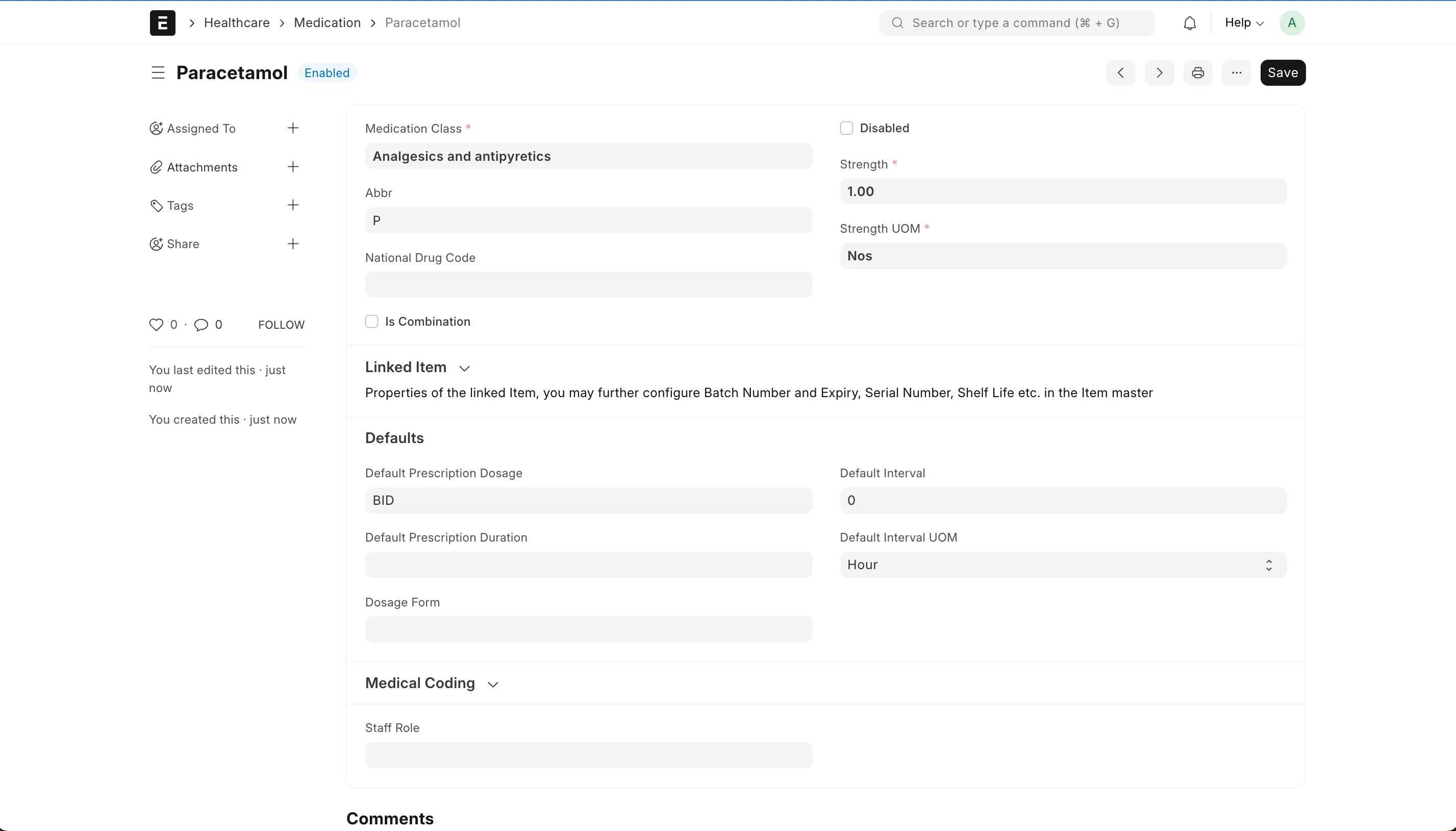
Also create a service request for a CBC lab test. Choose the order template for the test from the dropdown or create a new one.
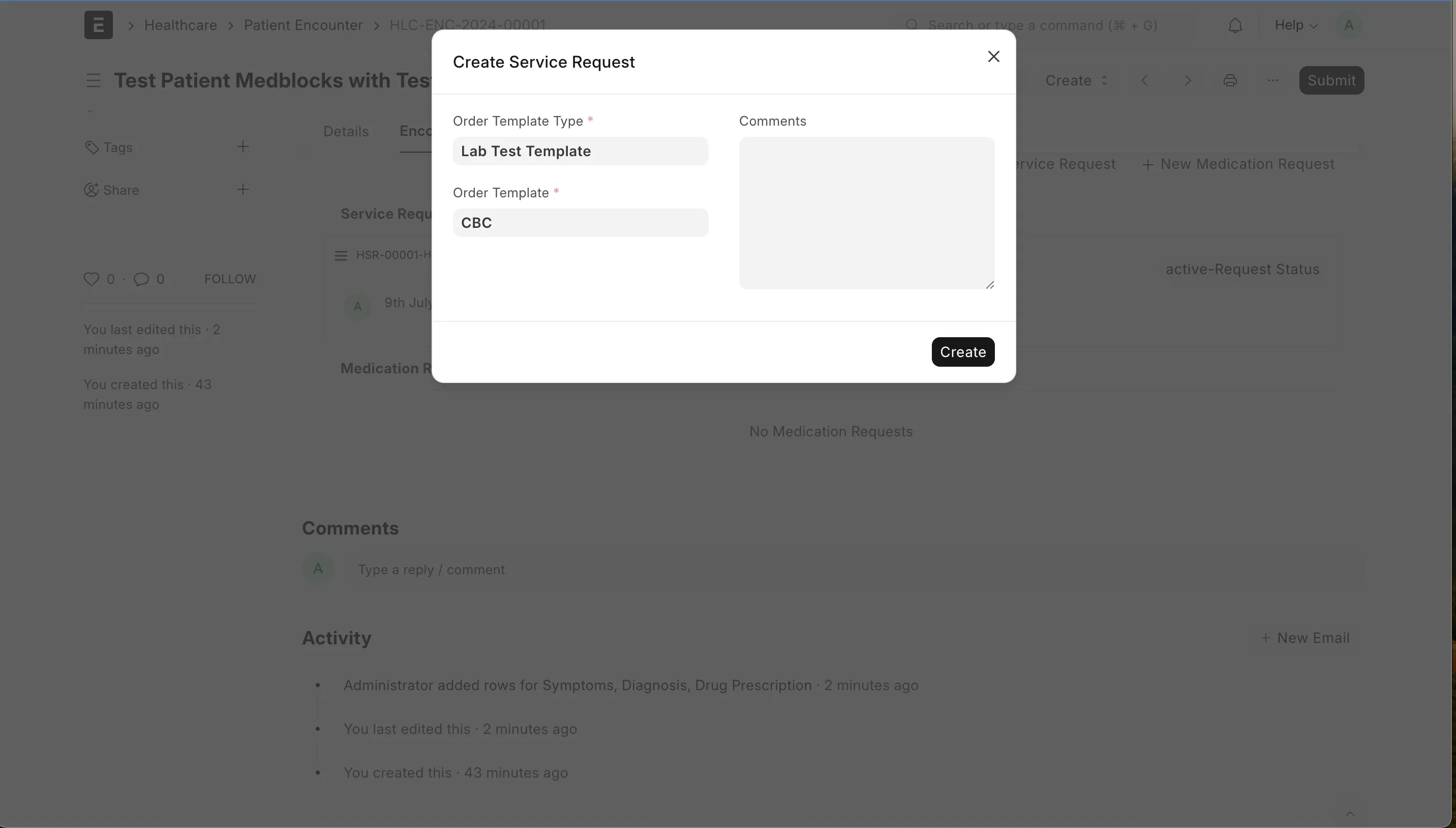
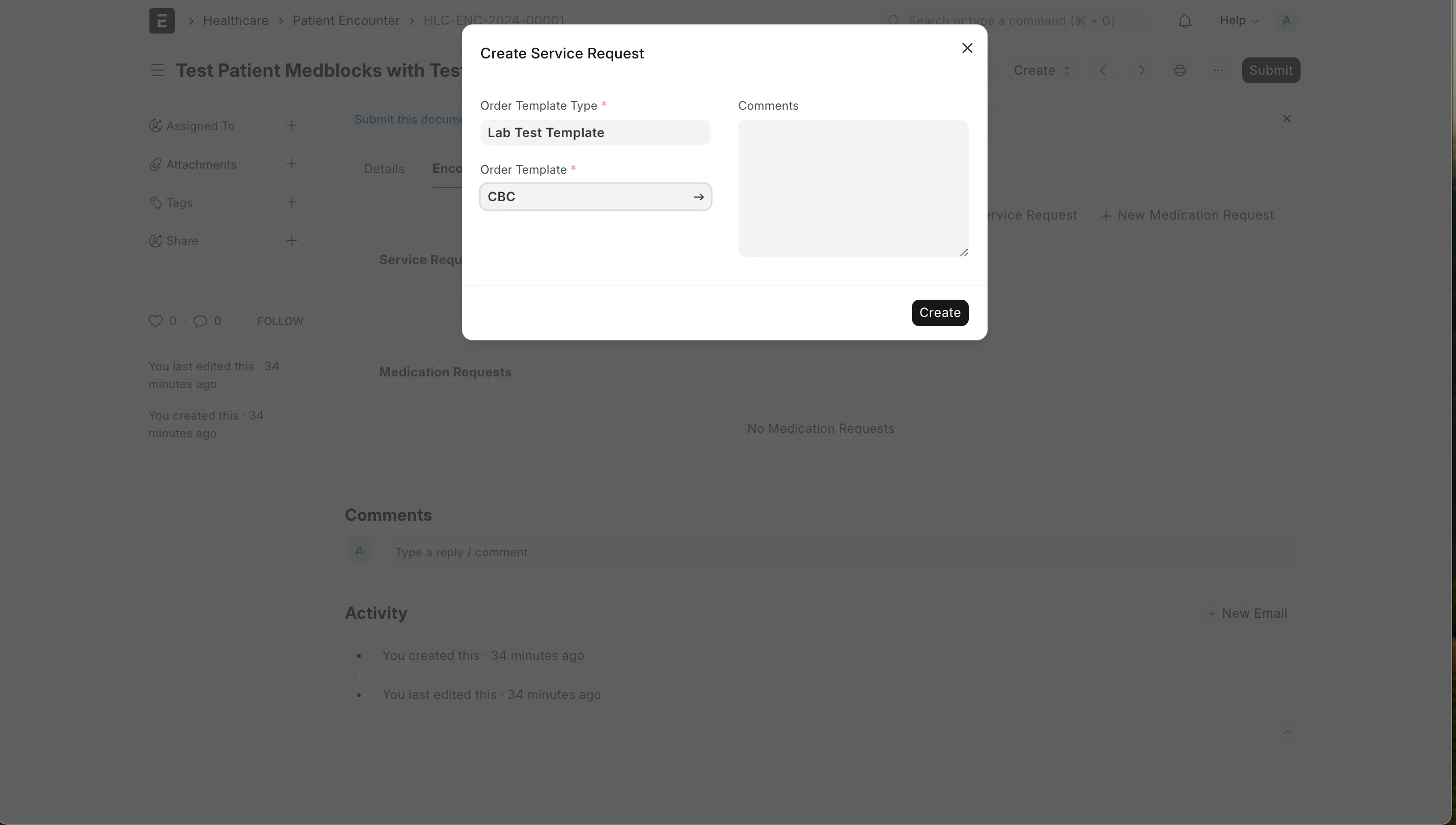
The final encounter view will look something like this.
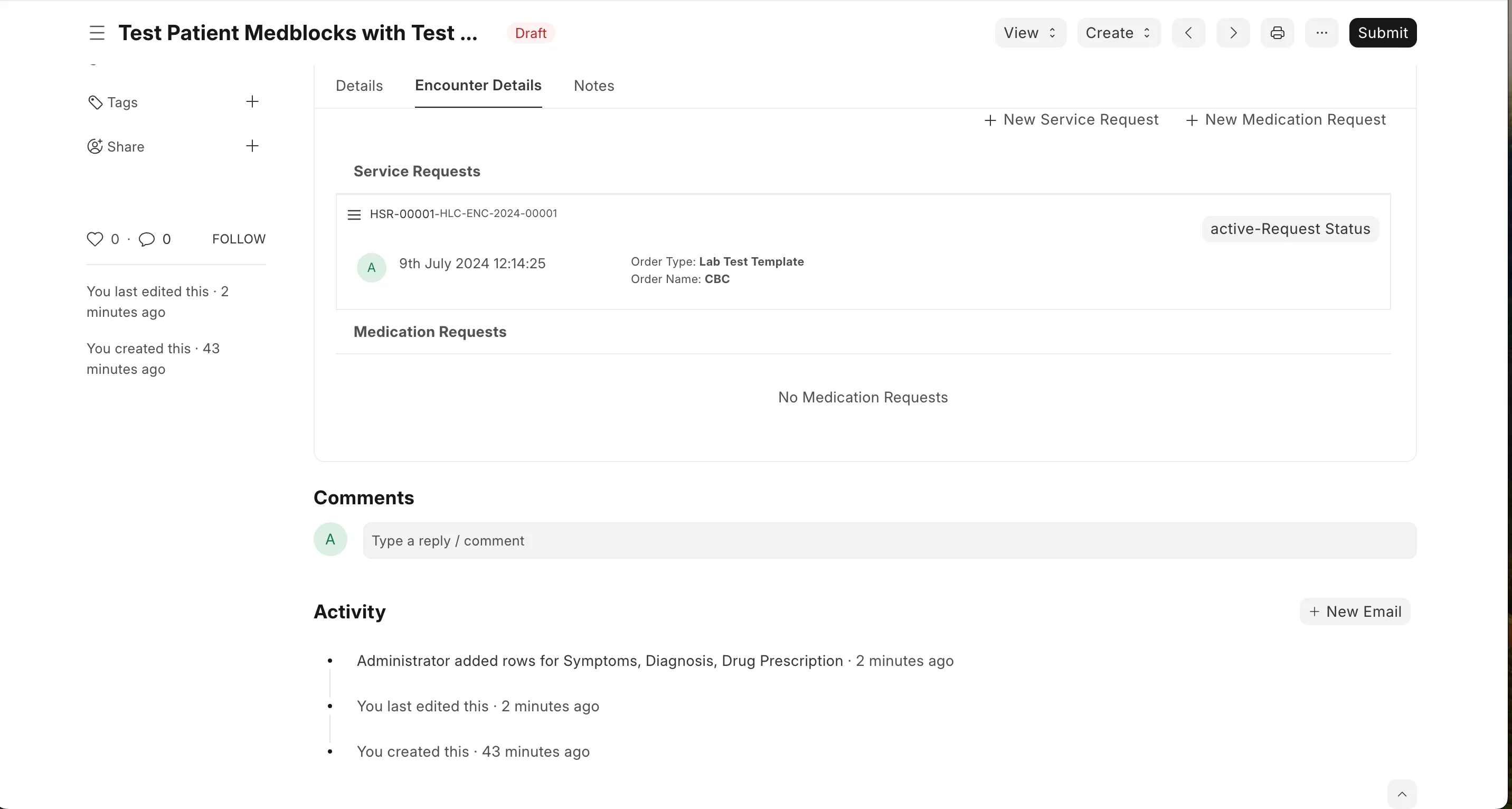
Verify all encounter details and click on final submit.
Create an Invoice
Once the encounter is finished, let’s create an invoice for the patient. The prescriptions can be fetched from Get Items From → Prescriptions . The service request from Get Items From → Healthcare Services .
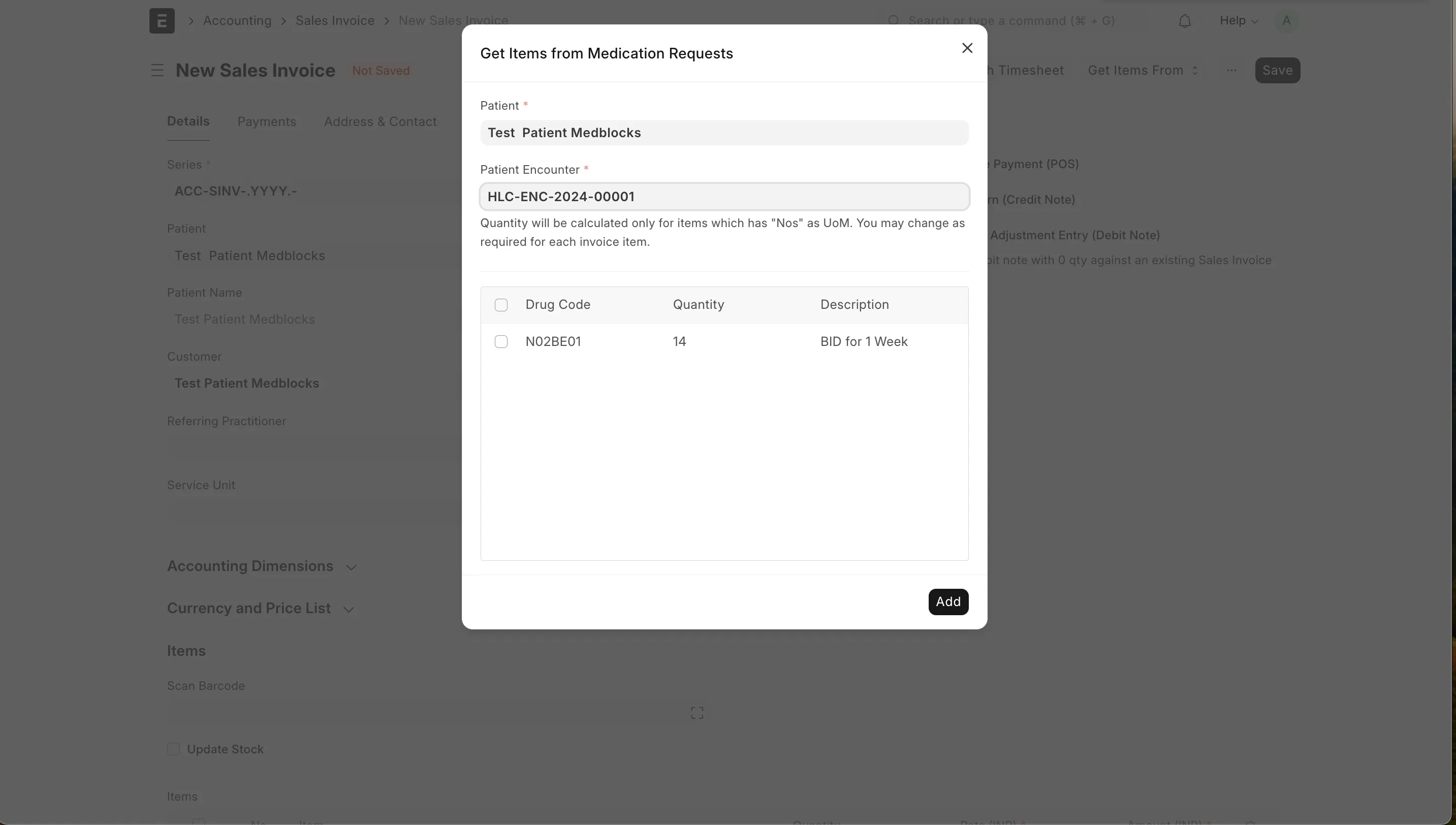
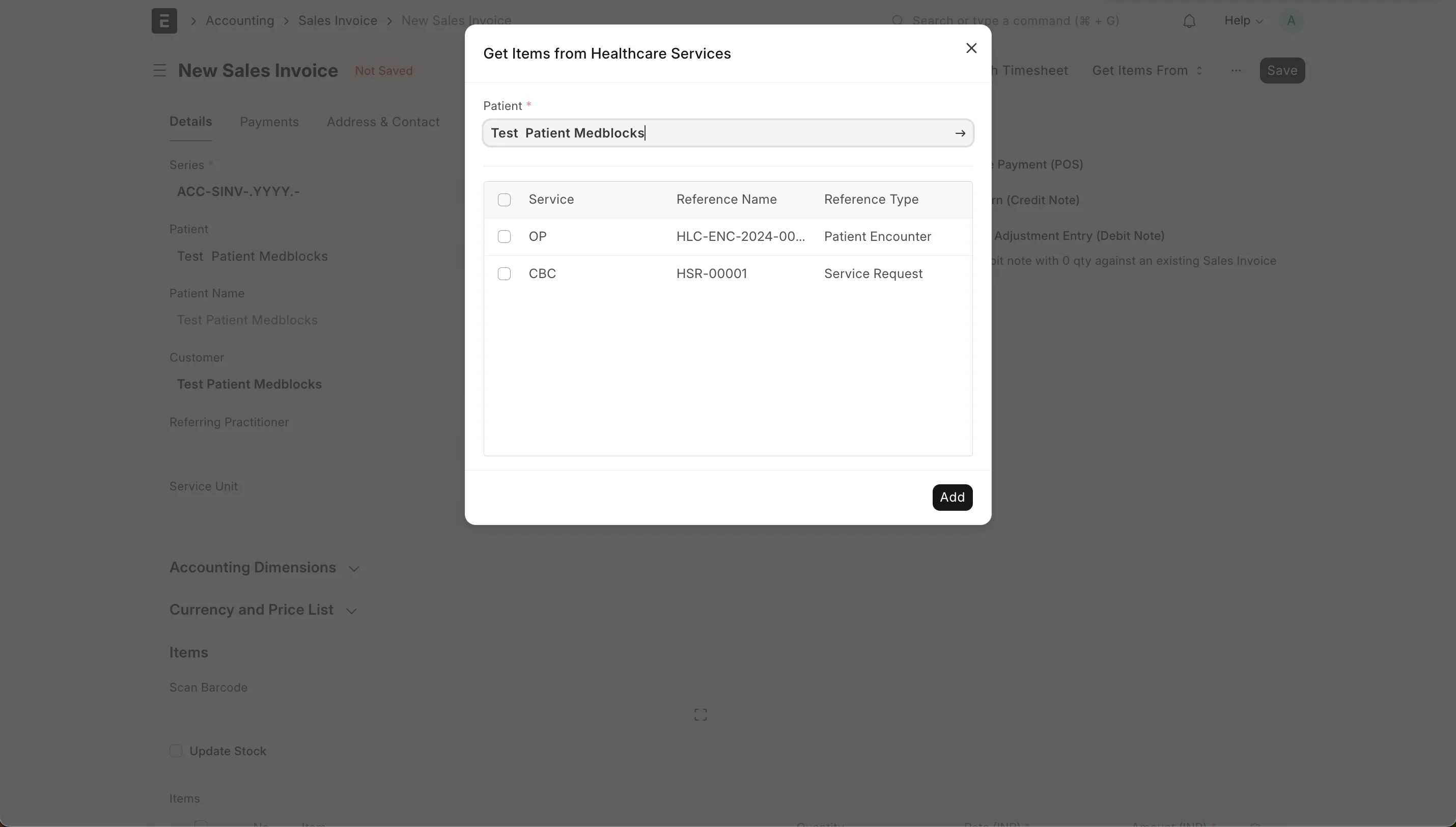
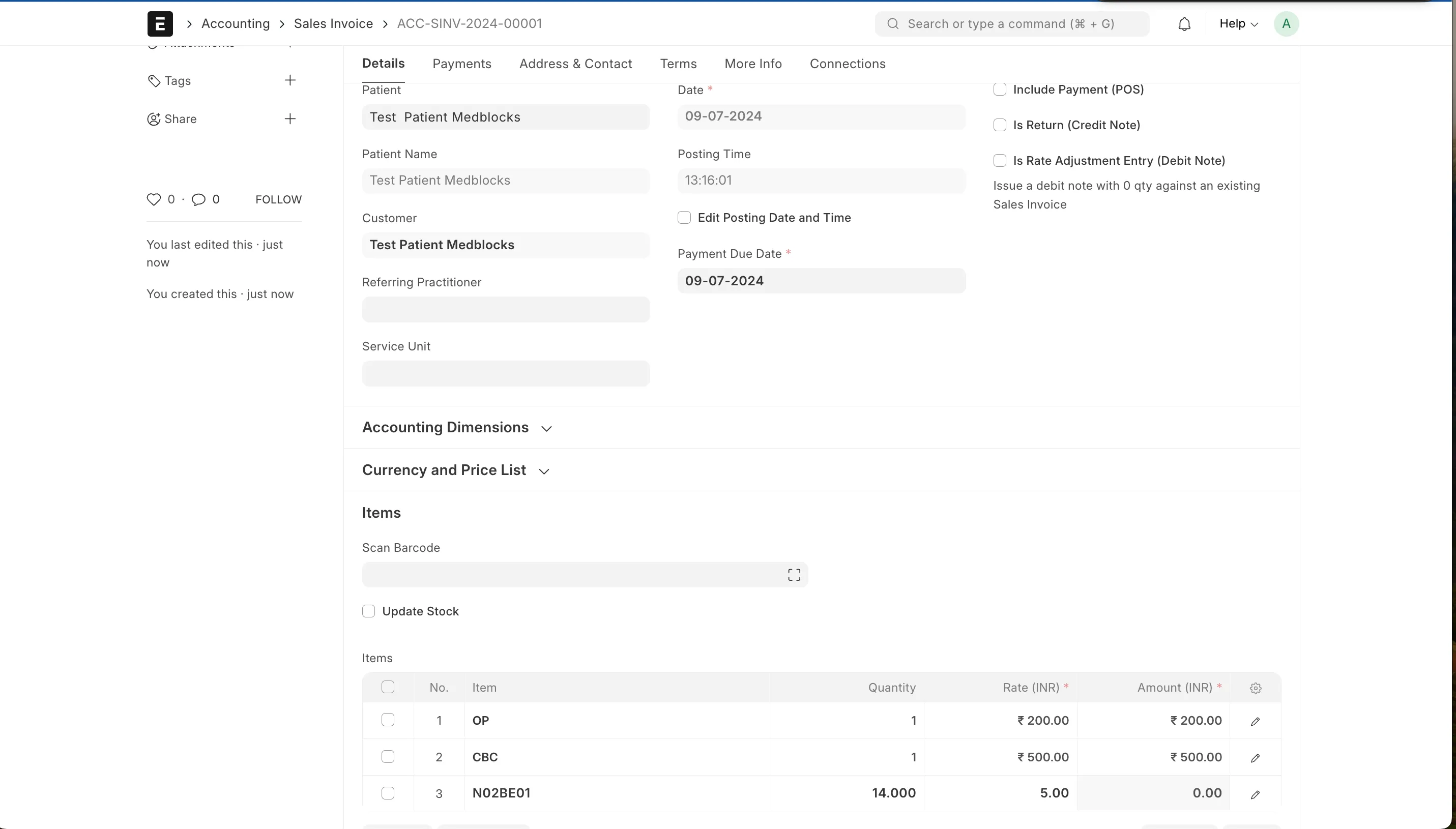
With all the charges pulled let’s save and submit the invoices.
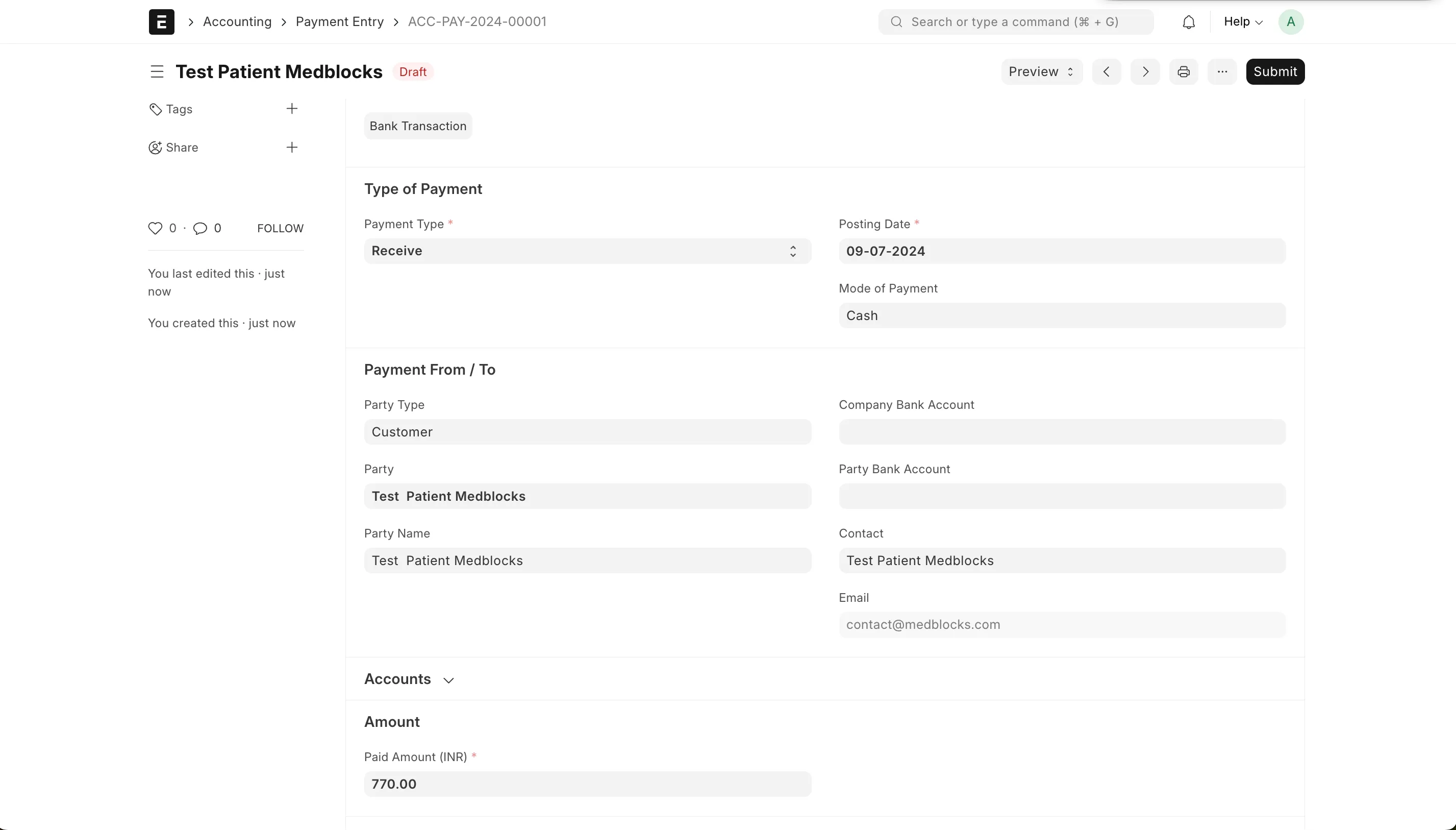
Now go to payments by selecting dropdown in Create button . You will navigate to Payment Entry docType. Review all the details then save and submit it to record successful payment.
We have now done an end to end demo of the out patient flow using ERPNext. As demonstrated above, ERPNext is capable of handling almost all requirements of your healthcare enterprise. And with the low-code, open-source nature of the platform you can easily suggest improvements or customise it for your needs.
Deploying ERPNext Healthcare on Kubernetes
In our early developmental phase, we used multiple Docker images and complex Helm charts to deploy the ERPNext application, which was tedious work. We then had a brilliant idea of consolidating it into a single Docker image and utilizing straightforward Kustomization files. This approach streamlined our deployment, making it more efficient and manageable.
Following are the insights and experiences that we gained. Let’s get straight into it.
-
Create a docker container with all the Frappe apps we want installed. Then pull the official ERPNext image. This will have both the Frappe bench and ERPNext installed on it.
-
Add the healthcare module to the bench. Let’s call this image
ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE.
FROM frappe/erpnext:v15.26.0
ARG APP_NAME=frontend
RUN bench get-app healthcare
CMD [ \
"/home/frappe/frappe-bench/env/bin/gunicorn", \
"--chdir=/home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites", \
"--bind=0.0.0.0:8000", \
"--threads=4", \
"--workers=2", \
"--worker-class=gthread", \
"--worker-tmp-dir=/dev/shm", \
"--timeout=120", \
"--preload", \
"frappe.app:application" \
] -
Set up the associated services required for Frappe, which includes the database, Redis, Gunicorn, and Nginx. Both Gunicorn and Nginx will be included in the Dockerfile as the frontend and backend dependencies. Although Frappe can work with both PostgreSQL and MariaDB, ERPNext does not fully support PostgreSQL, so we will use MariaDB as our database.
-
We have to add MariaDB as a StatefulSet using the
mariadb:10.6image. We will mount an init script, attach a persistent volume, and set a root password for the database.
Note: If you’re using a managed database provider like AWS RDS or Google’s Cloud SQL solutions, you don’t need to deploy a MariaDB instance within Kubernetes.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: mariadb-erpnext
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mariadb-erpnext
serviceName: mariadb-erpnext
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mariadb-erpnext
spec:
containers:
- name: mariadb
image: mariadb:10.6
args: ["--character-set-server=utf8mb4", "--collation-server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci", "--skip-character-set-client-handshake", "--skip-innodb-read-only-compressed"]
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
env:
- name: MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: mariadb_password
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/mysql
name: mariadb-storage
- name: mariadb-init
mountPath: /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d
volumes:
- name: mariadb-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mariadb-erpnext-storage
- name: mariadb-init
configMap:
name: mariadb-init
items:
- key: init.sql
path: init.sql
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: mariadb-erpnext-storage
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
storageClassName: standard
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi- As mentioned above, this MariaDB instance needs to be linked to storage named
mariadb-erpnext-storage. In this particular example, we are using Google Cloud, so we will utilise Google’s dynamically provisioned persistent volume.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mariadb-erpnext-storage
spec:
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce- Now let us deploy this db as a service in port 3306.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mariadb-erpnext
spec:
selector:
app: mariadb-erpnext
ports:
- port: 3306
targetPort: 3306
type: ClusterIP- Add the MariaDB files to
kustomization.yaml.
resources:
- maria.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: mariadb-init
files:
- init.sql- The
init.sqlfile used creates a user and db frappe.
create user if not exists 'frappe'@'localhost' identified by 'frappe';
grant all privileges on *.* to 'frappe'@'localhost' with grant option;
create database if not exists `frappe`;- Once done with MariaDb let’s set up the Redis instances. In Frappe we need the Redis for cache management, queue management and socketio. So we will have a deployment and service each. For this example we will use a open-source Redis image from valkey:
valkey/valkey:7.2.
redis-cache
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-cache
namespace: erpnext
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-cache
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-cache
spec:
containers:
- name: valkey-cache
image: valkey/valkey:7.2
command: ["valkey-server", "/etc/conf.d/redis.conf"]
resources:
limits:
memory: "500Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-config
mountPath: /etc/conf.d
volumes:
- name: redis-config
configMap:
name: redis-config
items:
- key: redis.conf
path: redis.conf
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-cache
spec:
selector:
app: redis-cache
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379redis-queue
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-queue
namespace: erpnext
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-queue
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-queue
spec:
containers:
- name: valkey-queue
image: valkey/valkey:7.2
command: ["valkey-server", "/etc/conf.d/redis-queue.conf"]
resources:
limits:
memory: "500Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
volumeMounts:
- name: redis-queue-config
mountPath: /etc/conf.d
volumes:
- name: redis-queue-config
configMap:
name: redis-queue-config
items:
- key: queue.conf
path: redis-queue.conf
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-queue
spec:
selector:
app: redis-queue
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379redis-socketio
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-socketio
namespace: erpnext
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: redis-socketio
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-socketio
spec:
containers:
- name: valkey-queue
image: valkey/valkey:7.2
resources:
limits:
memory: "500Mi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-socketio
spec:
selector:
app: redis-socketio
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379- Add the kustomization file for redis.
resources:
- redis.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: redis-config
namespace: erpnext
files:
- redis.conf
- name: redis-queue-config
namespace: erpnext
files:
- queue.confThe redis.conf file used.
bind 0.0.0.0
port 6379
loglevel notice
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lruThe queue.conf file used.
bind 0.0.0.0
port 6379
loglevel notice-
Now that we have all the microservices needed let’s deploy the main app. We will approach this by creating a stateful application for frontend and backend and deploying them as services.
-
The backend will have 5 containers - the main backend app, the socketio app, long and short queues and a scheduler. Of these, expose the main backend container and the socketio as services.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: erpnext-backend
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: erpnext-backend
serviceName: erpnext-backend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: erpnext-backend
spec:
containers:
- name: erpnext-socketio
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
node /home/frappe/frappe-bench/apps/frappe/socketio.js
ports:
- containerPort: 9000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- name: erpnext-backend
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- name: queue-long
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
bench worker --queue long,default,short
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- name: queue-short
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
bench worker --queue short,default
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- name: scheduler
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
bench schedule
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
volumes:
- name: erpnext-site
configMap:
name: erpnext-config
items:
- key: common_site_config.json
path: common_site_config.json
- name: erpnext-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: erpnext-storage
- name: erpnext-logs
emptyDir: {}
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: erpnext-storage
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: erpnext-backend
spec:
selector:
app: erpnext-backend
ports:
- port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
name: backend
- port: 9000
targetPort: 9000
name: socketio
type: ClusterIP- The front end will have a single container that listens to the backend and socketio services using a nginx gateway.
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: erpnext-frontend
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: erpnext-frontend
serviceName: erpnext-frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: erpnext-frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: erpnext-frontend
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command:
- nginx-entrypoint.sh
env:
- name: BACKEND
value: "erpnext-backend.erpnext.svc.cluster.local:8000"
- name: SOCKETIO
value: "erpnext-backend.erpnext.svc.cluster.local:9000"
- name: FRAPPE_SITE_NAME_HEADER
value: "frontend"
- name: UPSTREAM_REAL_IP_ADDRESS
value: "127.0.0.1"
- name: UPSTREAM_REAL_IP_HEADER
value: "X-Forwarded-For"
- name: UPSTREAM_REAL_IP_RECURSIVE
value: "off"
- name: PROXY_READ_TIMEOUT
value: "120"
- name: CLIENT_MAX_BODY_SIZE
value: "50m"
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
volumes:
- name: erpnext-site
configMap:
name: erpnext-config
items:
- key: common_site_config.json
path: common_site_config.json
- name: erpnext-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: erpnext-storage
- name: erpnext-logs
emptyDir: {}
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: erpnext-storage
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: erpnext
spec:
selector:
app: erpnext-frontend
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
name: frontend
type: ClusterIP
- With both backend and frontend deployment set up, let’s install the Frappe apps.
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: migrate-install-app
spec:
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
containers:
- name: erpnext-init-modify-files
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
cp -f /home/frappe/common_site_config.json /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites/common_site_config.json && \
cat /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites/common_site_config.json
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe
name: erpnext-site
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/logs
name: erpnext-logs
- name: erpnext-init-install
image: ERPNEXT_HEALTHCARE_IMAGE
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
ls -1 apps > /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites/apps.txt && \
bench new-site --no-mariadb-socket --admin-password=changeMePlease --db-root-password=mariadb_password --install-app erpnext --set-default erpnext-frontend --force && \
bench --site erpnext-frontend install-app healthcare
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/sites
name: erpnext-storage
- mountPath: /home/frappe/frappe-bench/logs
name: erpnext-logs
volumes:
- name: erpnext-site
configMap:
name: erpnext-config
items:
- key: common_site_config.json
path: common_site_config.json
- name: erpnext-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: erpnext-storage-v8
- name: erpnext-logs
emptyDir: {}- Also, create a PersistentVolumeClaim to attach the statefulSets.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: erpnext-storage
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 6Gi- Now let us add the ERPNext namespace to the directory.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: erpnext- Finally, let’s create a kustomization file for the main ERPNext folder. We also need to create a configMapGenerator to add the basic ERPNext configs from
common_site_config.json.
resources:
- namespace.yaml
- ./redis
- ./maria
- svc.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: erpnext-config
files:
- ./common_site_config.jsonThe common_site_config.json will look similar to:
{
"db_host": "mariadb-erpnext.erpnext.svc.cluster.local",
"db_port": 3306,
"db_name": "frappe",
"db_user": "frappe",
"db_password": "mariadb_password",
"redis_cache": "redis://redis-cache.erpnext.svc.cluster.local:6379",
"redis_queue": "redis://redis-queue.erpnext.svc.cluster.local:6379",
"redis_socketio": "redis://redis-socketio.erpnext.svc.cluster.local:6379",
"http_port": "8080",
"frappe_user": "frappe",
"admin_password": "changeMePlease",
"socketio_port": "9000",
"enable_frappe_logger": true,
"monitor": true,
}
This is the final folder structure.
├── erpnet
├── maria
├── db.yaml
├── init.sql
├── kustomization.yaml
├── redis
├── redis.yaml
├── redis.conf
├── queue.conf
├── kustomization.yaml
├── svc.yaml
├── namespace.yaml
├── common_site_config.json
├── kustomization.yaml-
With all the services configured and running, use any proxy to set up the frontend
erpnextservice on the domain of your choosing. Visit the configured URL and complete the initial setup to have a fully functional ERP solution with the healthcare module on your system. -
Push it all to your Kubernetes a
kubectl apply -k .command, or by using a GitOps solutions like ArgoCD or Flux.
Summary
In summary, the integration of ERPNext with a health data platform like Medblocks offers a well-rounded solution for healthcare providers. ERPNext’s customizable open-source platform efficiently manages patient care, inventory, billing, and the entire revenue cycle. Health data platforms built on standards like FHIR and openEHR are then well suited for capturing and storing clinical data. By deploying it on Kubernetes, Medblocks ensures the system is both scalable and easy to manage. This solution enables healthcare institutions to streamline their operations and enhance patient care effectively while maintaining data standards.
If you’re interested in setting up ERPNext or Health data platforms for your next healthcare venture, click on the link below to contact us.
