Are you struggling to understand the openEHR CKM interface? Here’s a beginner-friendly walkthrough on how to search, view and download clinical artefacts easily.
The openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager (CKM) is a global repository of archetypes and templates that are maintained and updated by a community of healthcare and informatics professionals. The artefacts in the CKM are open-source and available for use under a Creative Commons license. In this way, the CKM enables the reuse of clinical artefacts, allowing for openEHR to be used as a common standard and language, promoting interoperability.
In this article, we will look at how to navigate and use the CKM, including how to search, view and download clinical artefacts including archetypes, templates and termsets (terminology reference sets). First, let’s take a look at the CKM home screen and identify key panes.
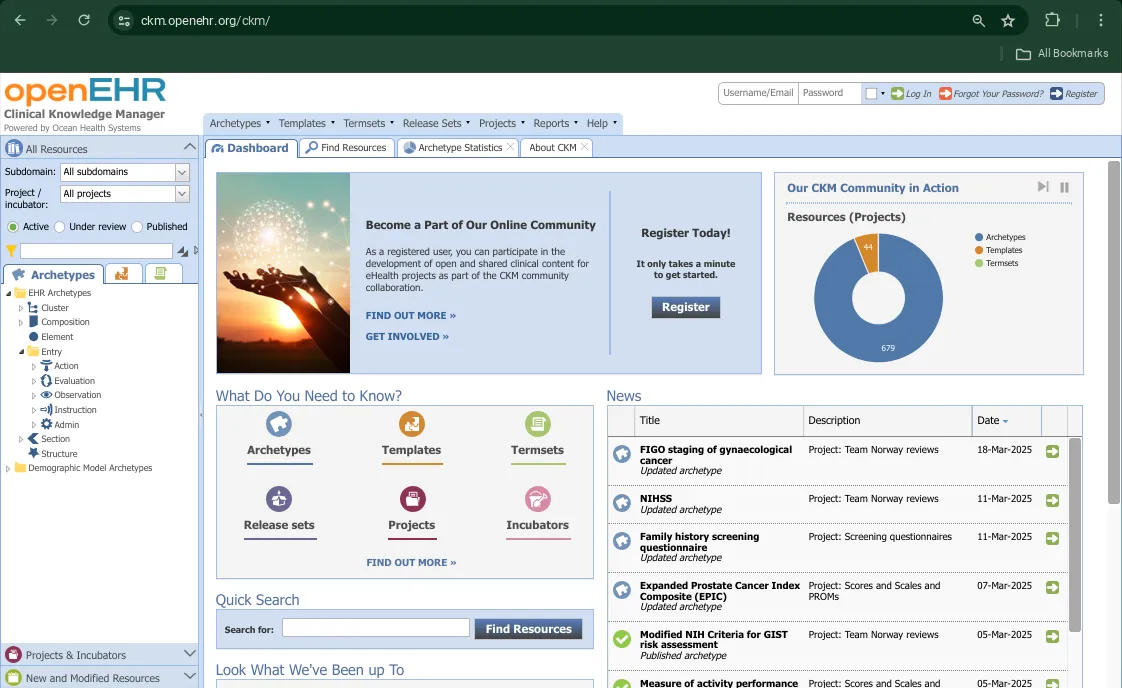
- The Accordion Menu on the left contains the sections
All Resources,Projects & IncubatorsandNew and Modified Resources - On the top right, you can see options to Log In or Register as a new user
- The Dashboard contains an overview of key information such as CKM community updates, news, summaries of the artefacts present in the CKM, quick links to all important sections of the portal and a search bar
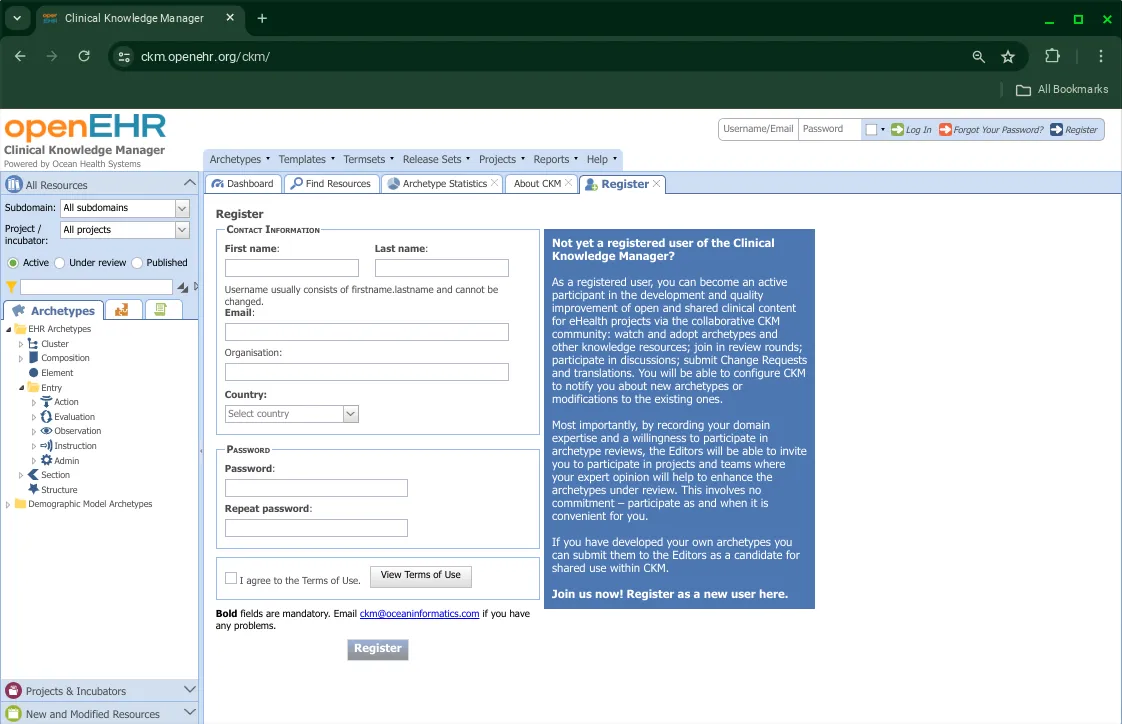
Registering as a user of the CKM is easy, and a great way to become an active participant in the development and improvement of clinical health artefacts. This registration form opens up on clicking the Register button.
Searching for clinical artefacts on the CKM
Finding the appropriate artefact for your clinical implementation is essential in ensuring data accuracy and meaningful decision making. This way, healthcare data remains standardized and reusable and leads to better interoperability. There are several ways to search for artefacts in the CKM, including, quick search, the find resources tab, the project sub-tab in the find resources tab, the All Resources Pane, and the Project accordion heading in the left panel. We’ll be looking at each of these options one by one.
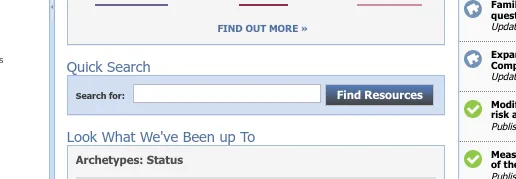
Option 1: The Quick Search widget on the CKM Dashboard
The CKM dashboard contains a widget labelled Quick Search, that allows you to search for artefacts with the default search settings. Enter your query into the text box, and click ‘Find Resources’.
Option 2: Using the Find Resources Tab
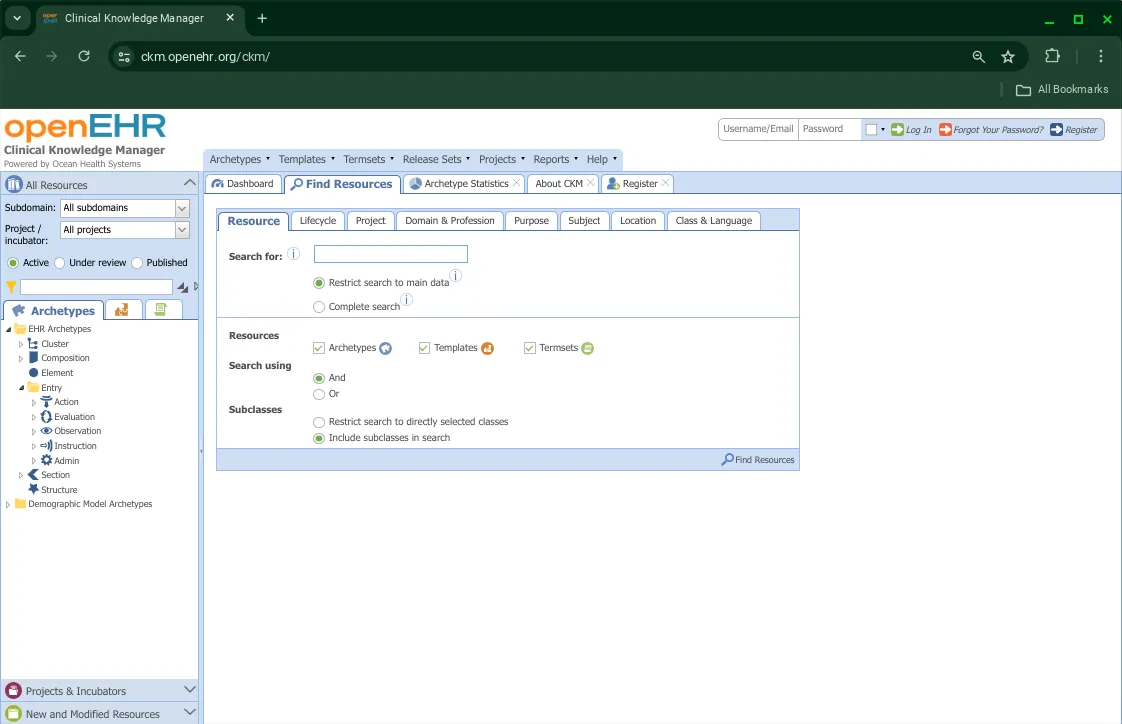
To perform a search,
- Ensure that the ‘Resource’ tab is selected - this is the default selection
- Enter your search query in the ‘Search for’ field
- Searches are case sensitive
- You can use * and ? as wildcards for partial search
- Set appropriate search parameters such as,
- ‘Restrict search to main data’ or perform a ‘Complete search’: The former is faster, while the latter also searches individual elements of archetypes
- Select one or more ‘Resources’ you want to search for, Archetypes, Templates or Termsets
- Connect search terms using ‘AND’ or ‘OR’. e.g. ‘blood’ AND ‘pressure’ to find ‘blood pressure’
- Include or restrict ‘Subclasses’ from your search
- Click
Find Resourcesor hit the Enter key to get search results
You can also search using the Project sub-tab under the find Resources Tab.
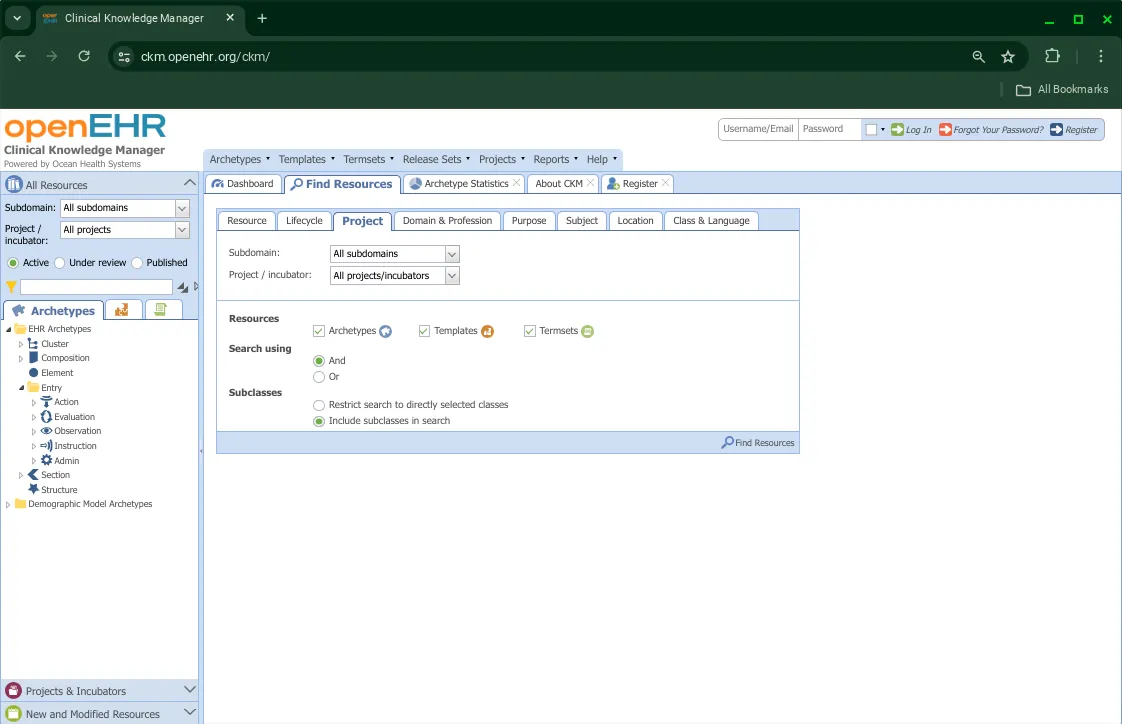
Most options remain the same except that you can also select the Subdomain and Project to search within. Selecting the Subdomain will limit the Projects shown in the dropdown.
Option 3: Using the All Resources panel
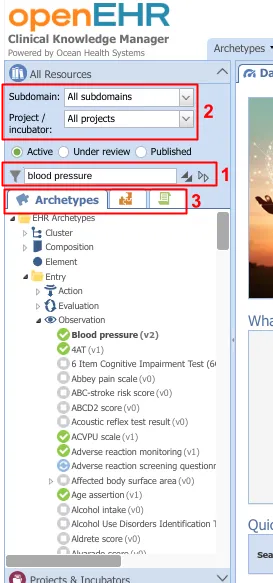
The left panel also allows you to search for clinical artefacts, in the search bar indicated by (1) in the image below.
- Clicking the funnel icon on the left of the search bar displays all resources, but marks your search results in bold as in the image.
- It is also possible to search in this panel by restricting the Subdomain and Project from the dropdowns present above the search bar, indicated by (2).
- Additionally, you can filter for archetypes, templates or termsets using the tabs placed below the search pane, indicated by (3).
Selecting the Projects & Incubators heading in the same panel, allows you to search by Projects and Subdomains. Your selected options will open up on the right pane.
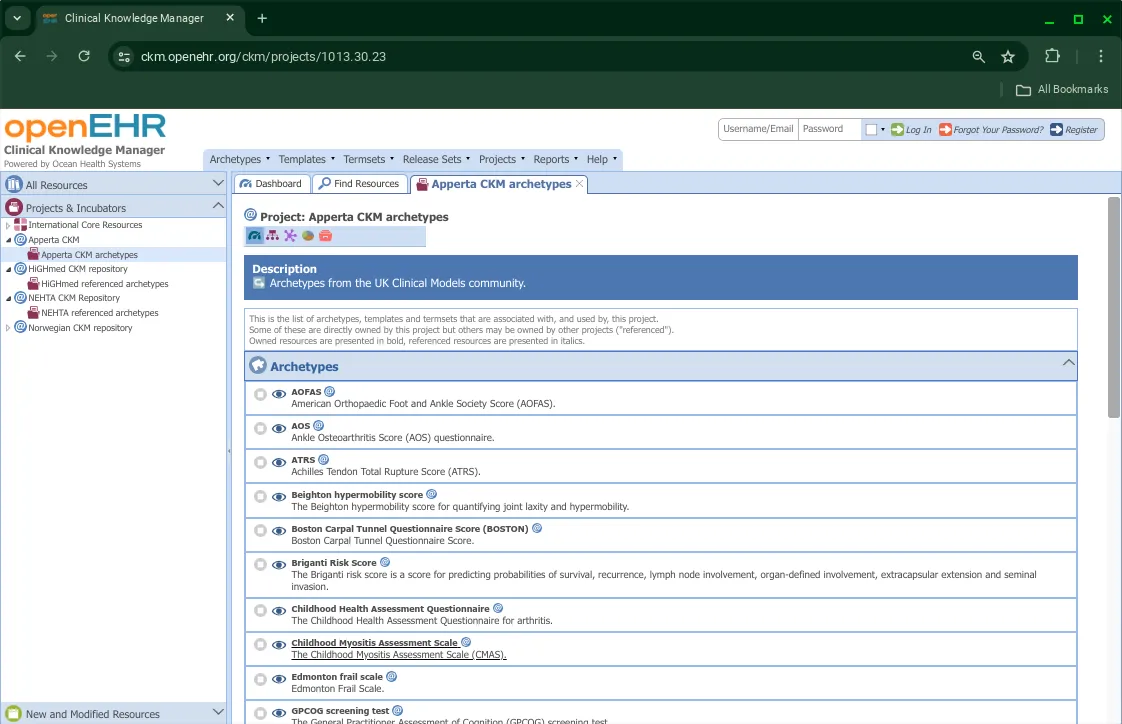
Option 4: Using the Projects Menu from the top Menu bar
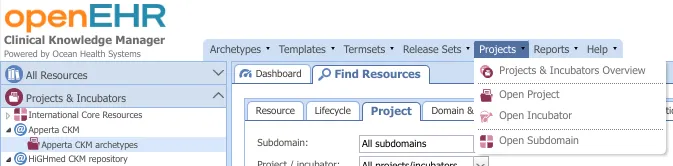
- Select
Projectsfrom the top menu bar - Select
Open Project. This opens up a window with a dropdown menu that lets you select from the projects available
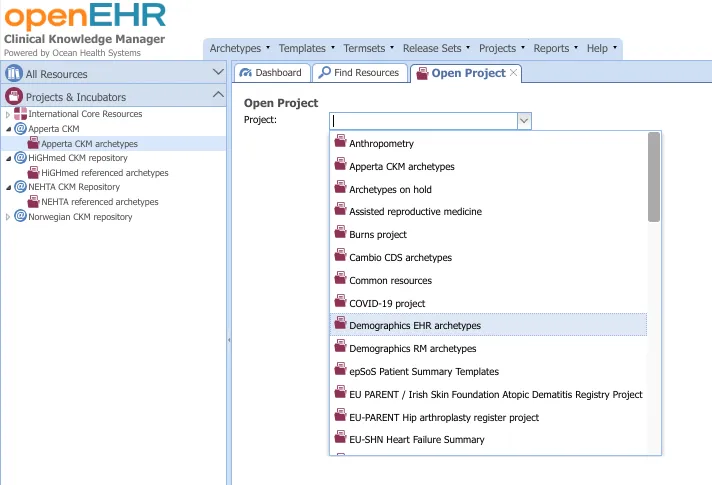
- Selecting a project opens it up in the right pane
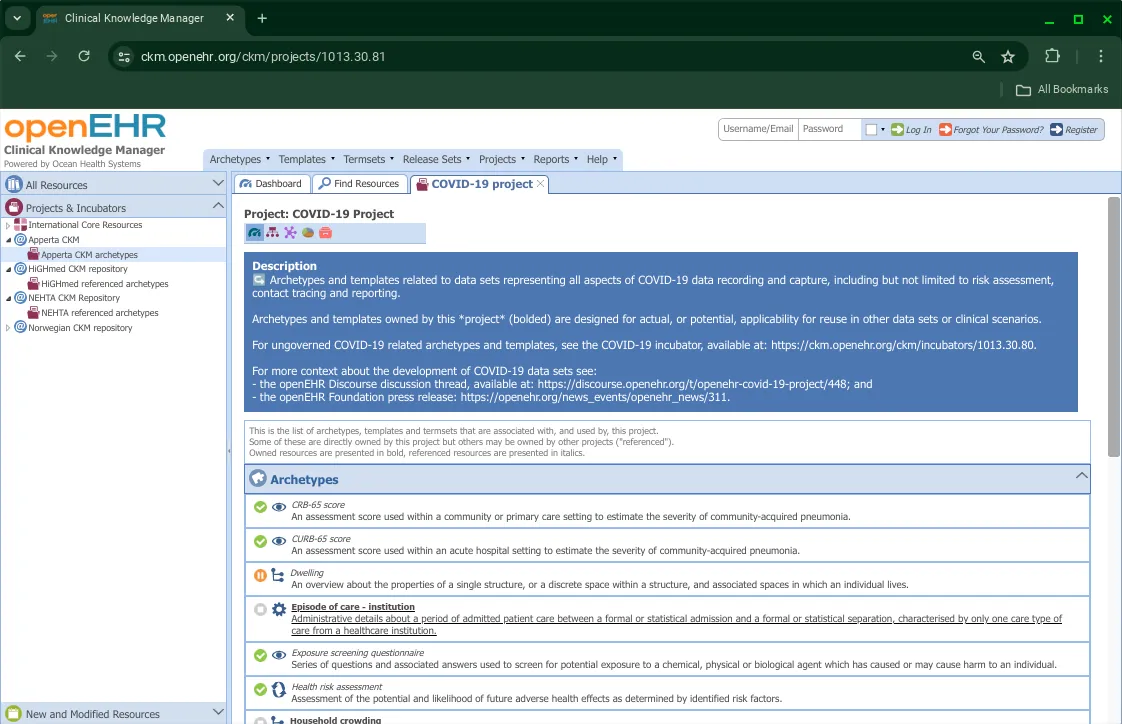
View a Project
Viewing clinical artefacts on the CKM
The CKM offers different ways to view information regarding clinical artefacts such as archetypes, templates and termsets. We’ll look at each of them one by one.
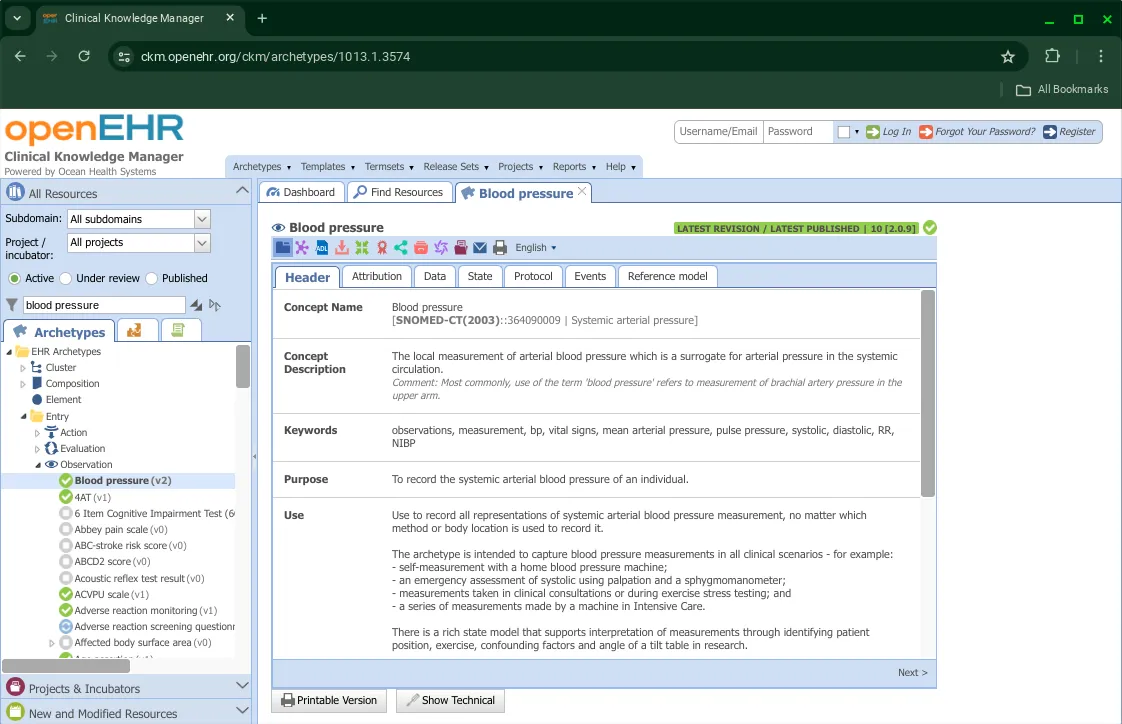
Viewing archetypes
On selecting an archetype, the default view that opens up is the Tabbed View. By navigating between each tab, you can view the headers, attributes, data, state, protocol, events and reference model of the archetype.
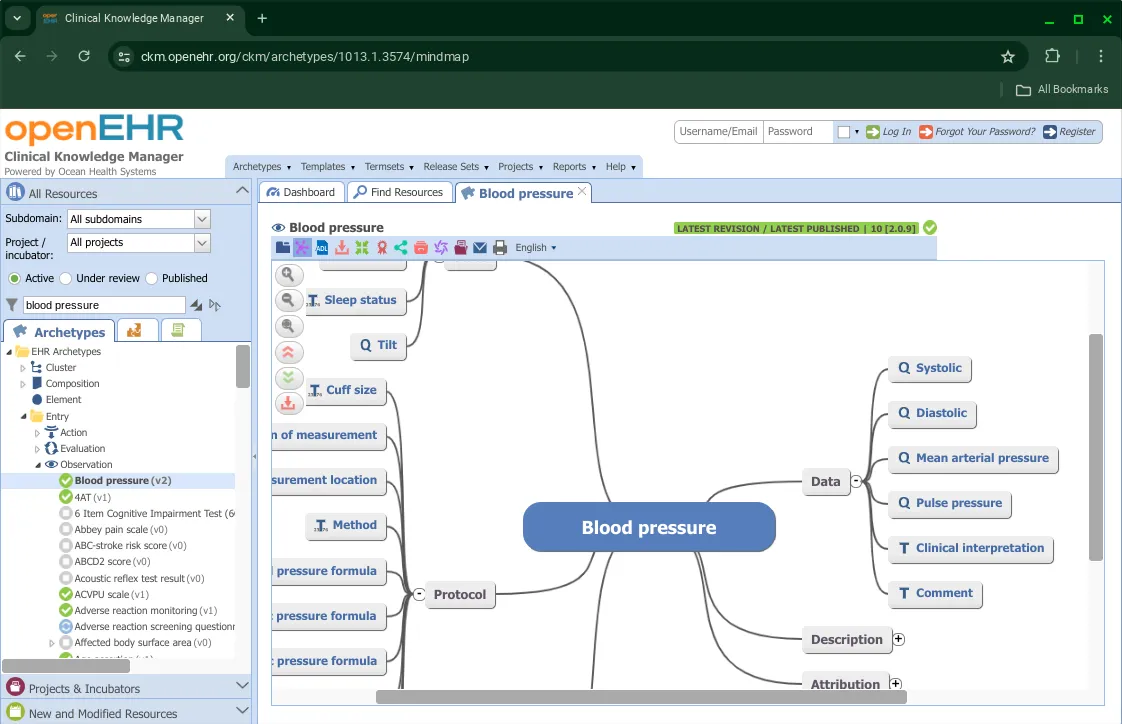
The second option available is the Mind Map view that pictorially depicts the archetype.
Viewing templates
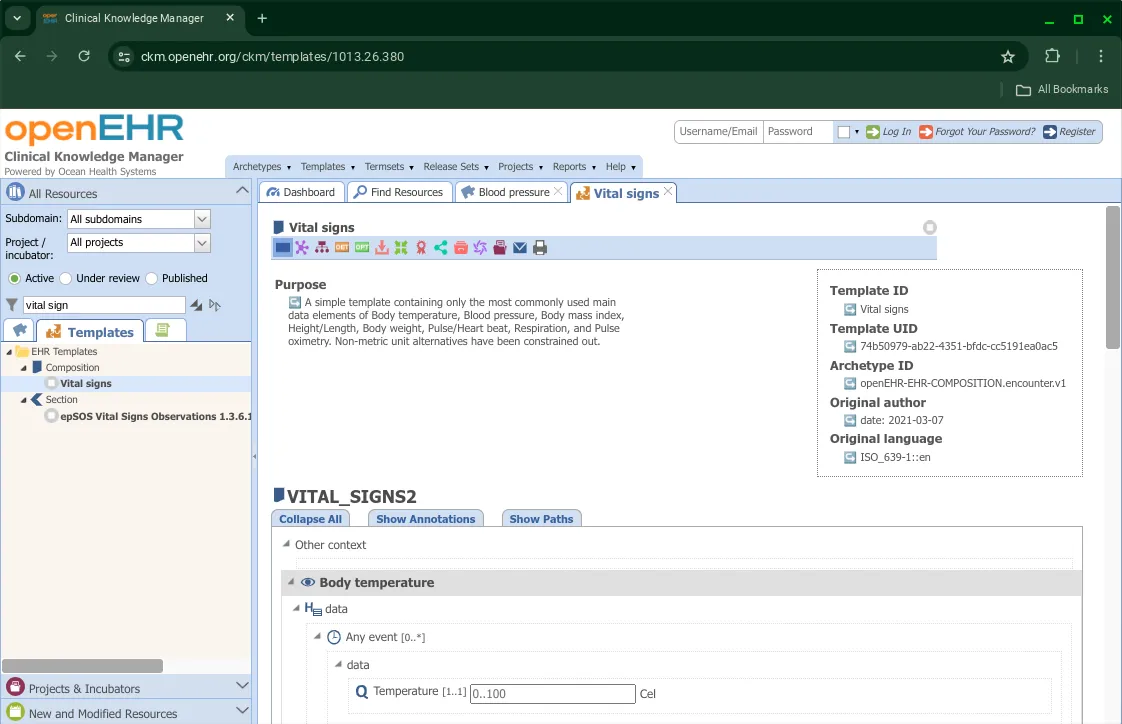
The default view for templates is the Simple View. This shows the purpose of a template, its identification information and all its contents below
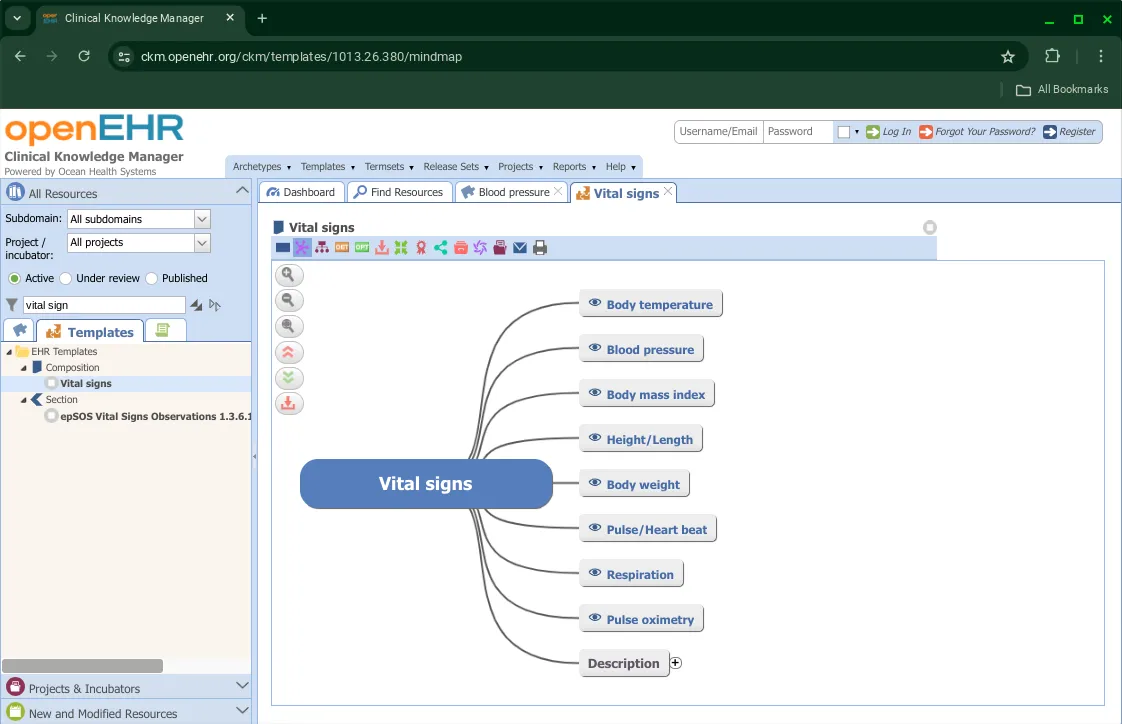
Here too, a Mind Map view is available.
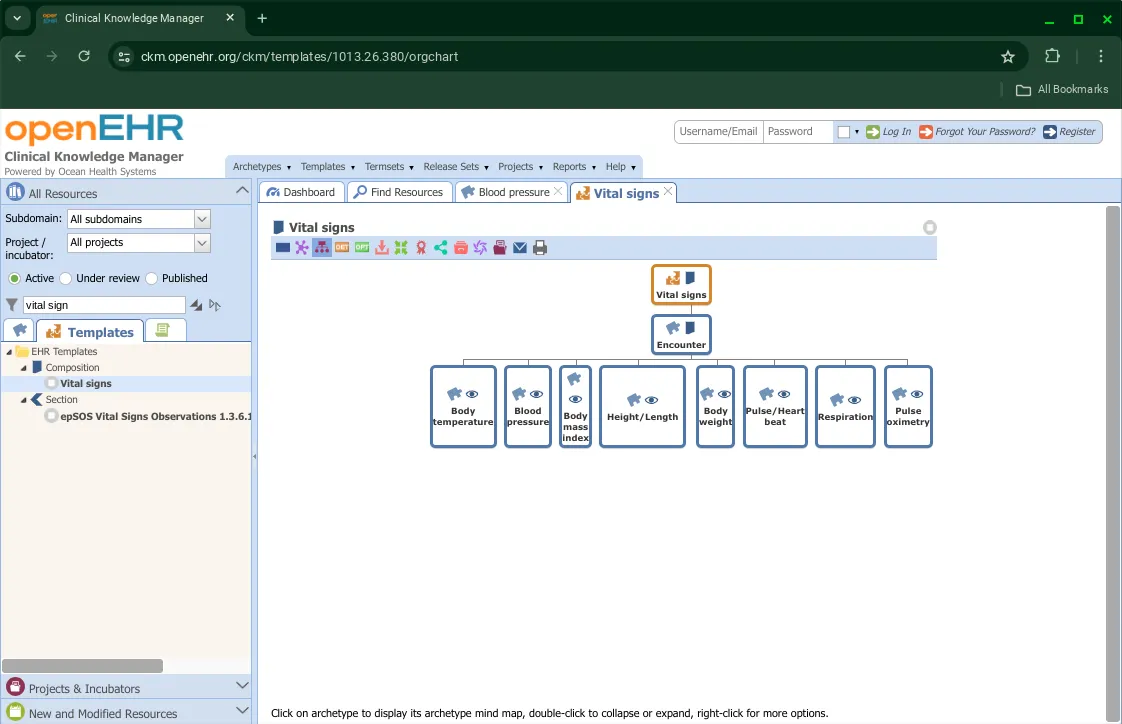
A third option is the Hierarchy view. Clicking on each archetype opens a pop-up window that shows its Mind Map view.
Viewing termsets
can also be searched and viewed in a similar way. The default view for a termset is a Simple View: Termset Result.
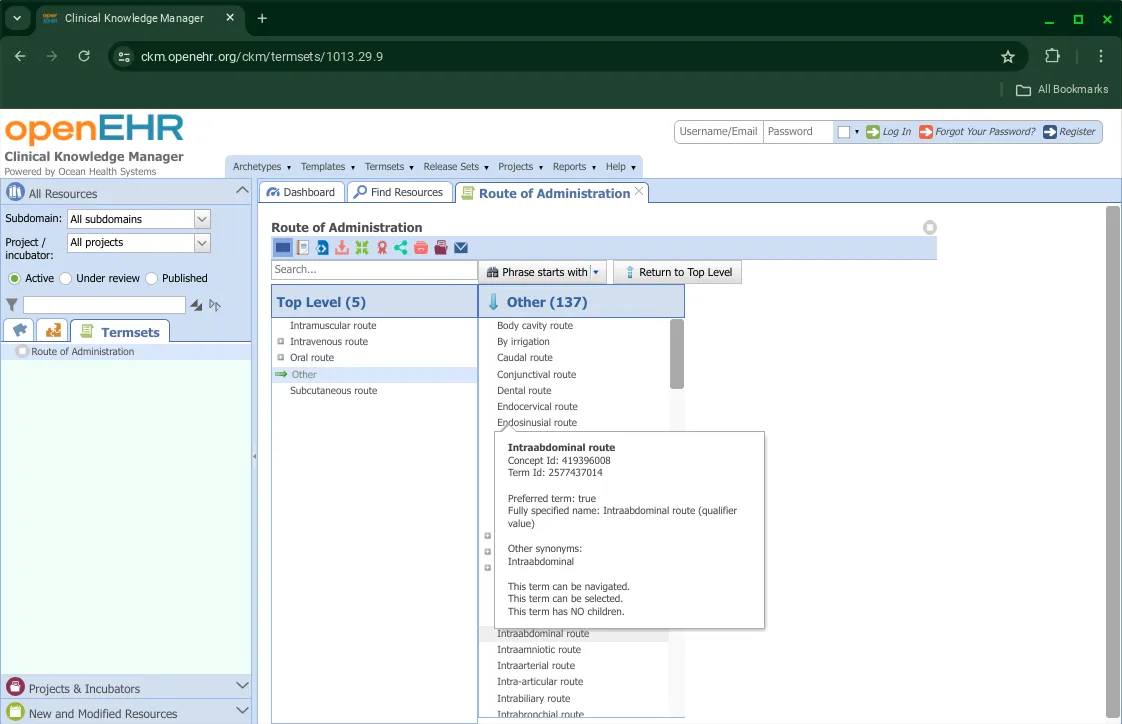
There are further options available to see the Rendered Termset Query and Termset Query XML.
Downloading clinical artefacts from the CKM
You often need to download clinical artefacts from the CKM in order to develop or extend EHR systems, map to external standards, modify or customize artefacts or for offline review and development. Here is how to download them.
Downloading archetypes
Archetypes have to be downloaded in order to reuse them in building templates.
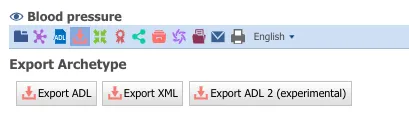
You can also perform a bulk download of archetypes
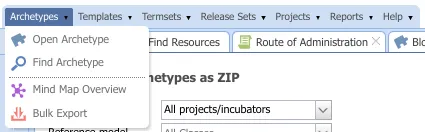
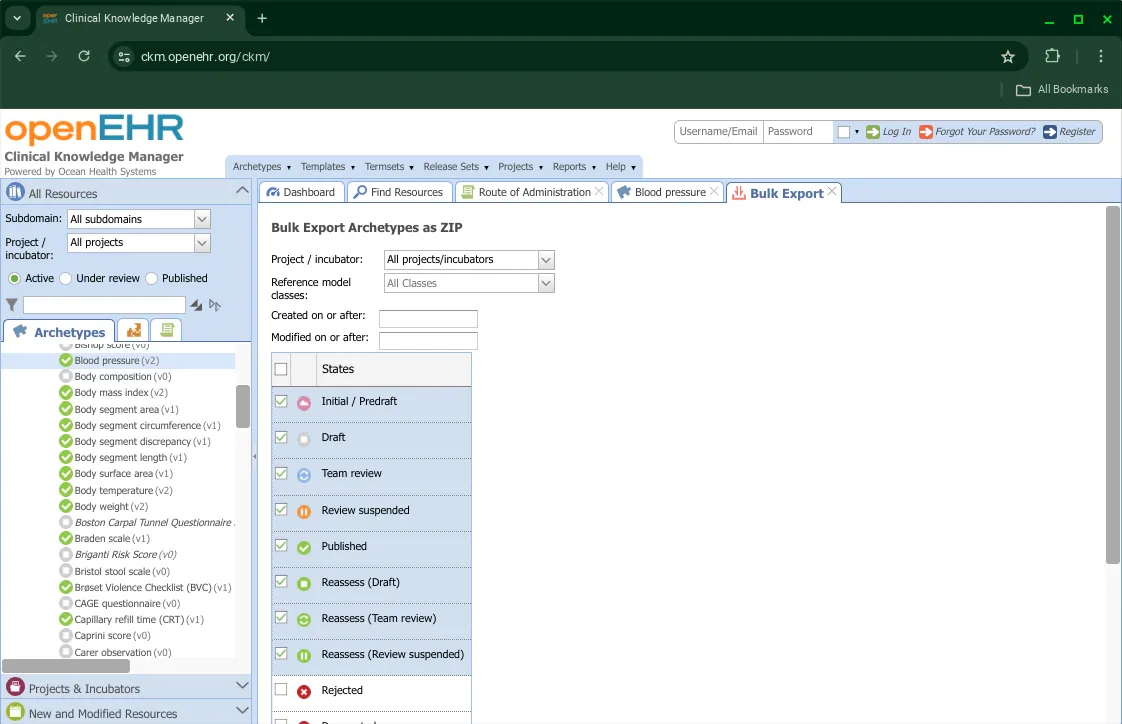
The Bulk Export option allows you to filter archetypes by Project, Reference Model Classes, date of creation and modification and state.
Downloading templates
Templates can be downloaded as an OET, Operational Template (OPT), Template Data Schema (TDS) and Template File Set as a zip file. For additional information, in this article, we differentiate between OET and OPT.
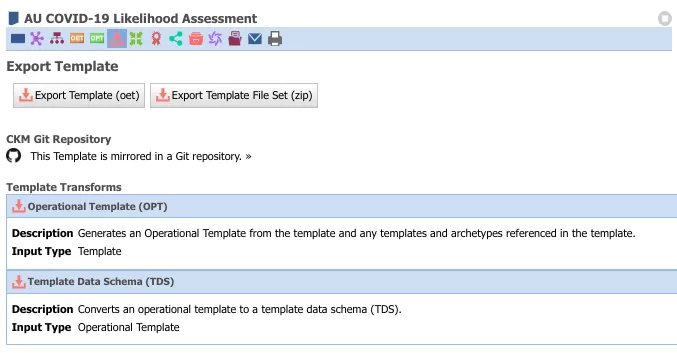
A similar Bulk Export option is also available.
Downloading termsets
Termsets can be downloaded in the XML format in a similar manner. They also have a Bulk Export option.
Final thoughts
Understanding how to use the Clinical Knowledge Manager(CKM) can speed up the process of implementing your own openEHR-based health IT system. Key functionalities like searching, viewing, and downloading are simple and easy to execute, with multiple options that cater to your exact needs. Join our free openEHR Fundamentals Course if you’re looking for a headstart in understanding and implementing openEHR.

