From archetypes to real world applications, learn how the Clinical Knowledge Manager enables openEHR implementations and empowers innovation through simplified collaboration.
As a leading open standard for electronic health records (EHRs), openEHR enables interoperability and long-term, vendor-neutral health data storage for health informatics. Key features of openEHR are the two-level data model, archetypes and templates that allow users to easily access and implement these standards according to their local requirements. The Clinical Knowledge Manager(CKM) is an important part of the openEHR ecosystem, as a global repository where healthcare professionals collaborate to develop and refine archetypes and templates. In this article, we will cover what the CKM is, why it is important, the evolution of the CKM, governance structures and community roles.
What is the Clinical Knowledge Manager?
First released by Ocean Health Systems in 2009, the openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager(CKM) is an international, online clinical knowledge resource. Powered by an active community of interested individuals from all over the world, the CKM contains over 900 active openEHR archetypes in 34 languages along with information on their publishing status, creators and contributors. All CKM content is open source and freely available under a Creative Commons license.
The CKM provides governance of openEHR knowledge artifacts, with established workflows defining the management, review, approval and maintenance of these artifacts in order to ensure accuracy, consistency and interoperability across healthcare systems. Every archetype or template follows a structured lifecycle including drafting, review, consensus approval, versioning and updates, ensuring they are clinically valid, high quality and reusable. It also prevents fragmentation and reduces duplication of efforts.
For information on how to use the CKM, this guide can help you get started.
Why is the Clinical Knowledge Manager important?
The CKM plays an important role in facilitating and managing health data interoperability, standardization, collaboration, governance, reusability and scale.
- Enables standardization and interoperability The CKM ensures consistency in data models by storing archetypes and templates and promoting their reuse across different healthcare settings. This ensures that the same clinical concept has the same meaning across different hospitals, countries and languages. It integrates with internationally recognized terminologies such as SNOMED CT, LOINC, ICD, FHIR etc. allowing structured and meaningful health data storage and exchange.
- Supports collaborative clinical modeling The CKM allows domain experts such as clinicians, informaticians and developers to collaborate on defining high quality clinical models, ensuring that the archetypes and templates reflect real world clinical needs as much as possible. It also helps to prevent duplicate and conflicting models, resulting in reduced fragmentation in healthcare data modeling.
- Ensures governance and quality control It manages the lifecycle of archetypes and templates, providing version control, approval workflows and governance mechanisms to ensure that clinical models stay updated and validated. Any new archetypes added to the CKM go through iterative peer review before they are approved. These processes also implement data reliability and integrity.
- Facilitates reusability and scalability
The CKM reduces duplication of effort by providing an open and free shared repository of validated clinical models, thereby each organization does not have to reinvent the wheel. Archetypes that have been approved and published can be reused in multiple settings, saving time and effort. This also makes it easier to scale for national and global implementations, allowing countries and organizations to customize templates without compromising on interoperability.

Functions of OpenEHR CKM
Evolution of the Clinical Knowledge Manager
The evolution of the Clinical Knowledge Manager started in 2005 with the Archetype Finder and was focused on archetypes. By 2007, the initial development of the CKM as we know it today began, and it recognized the need for a common platform to review and publish openEHR archetypes internationally. Its initial focus upon release in 2009 was threefold,
-
creation of an archetype library;
-
development of a formalized review process to achieve content consensus and archetype publication; and
-
governance of archetypes.
Support for Templates was incorporated in 2010, allowing multiple archetypes to be combined and edited according to local requirements. In addition, terminology subsets such as SNOMED CT, LOINC, ICD etc. were also incorporated in 2010, allowing linking archetypes with international terminologies.
Further governance improvements were made in the upcoming years including structured peer-review workflows and multi-stage approvals processes that ensured clinically validated, high quality archetypes. Version control mechanisms and consensus-driven approvals were introduced that allowed updates to models while maintaining historical integrity.
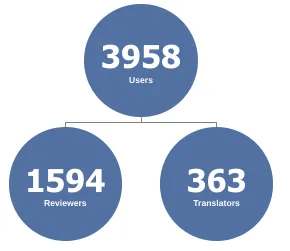
The CKM community now consists of over 3000 users across 119 countries, of which 1500+ are reviewers of submitted clinical data models. This community of clinicians, informaticians and software developers are a core strength in the continued improvement and adoption of openEHR and the openEHR CKM.
The COVID-19 pandemic was a significant turning point for the openEHR CKM, triggering a collaborative openEHR community effort to fast-track both archetype and template development related to the pandemic. The CKM was used as a coordinating hub in this effort, establishing it as a flexible and scalable tool for health data standardization.
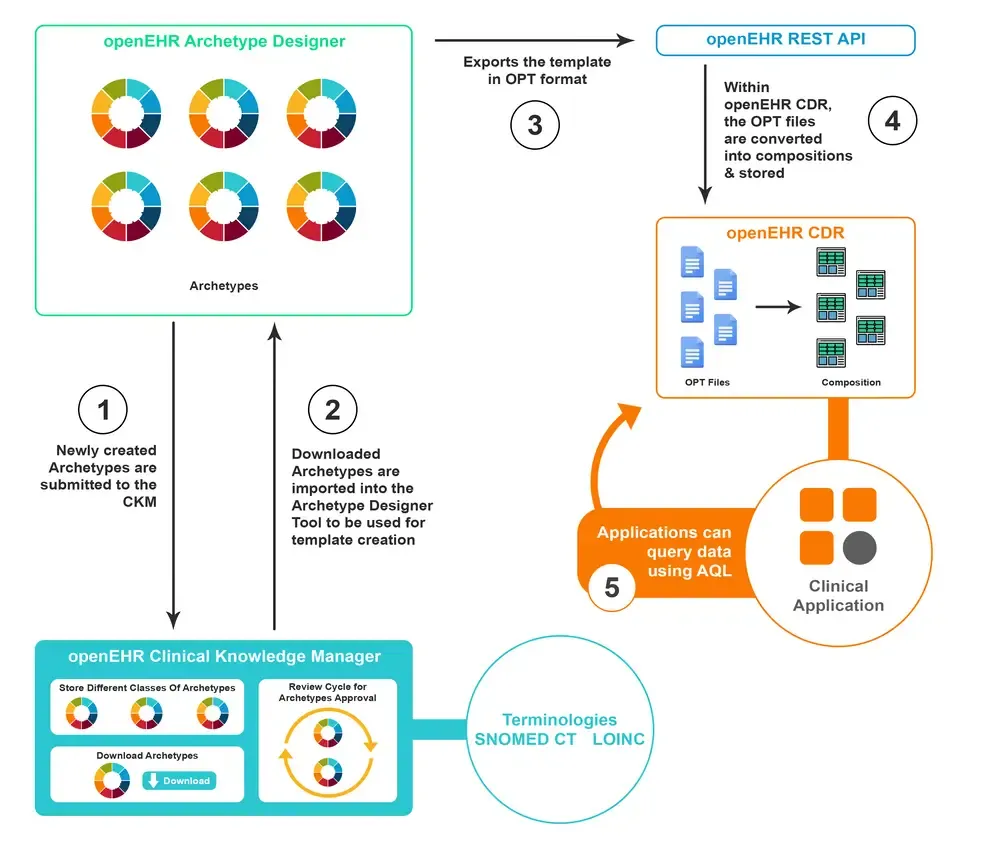
This is how the CKM fits in to the openEHR tool ecosystem:
What are the CKM governance environments?
Instances

CKM Instances are separate, region or organization specific deployments of the openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager. These local instances allow for adapting artefacts to local clinical guidelines, languages and regulatory requirements. The HiGHmed CKM for the German HiGHmed Consortium, the Norwegian CKM, Australian Digital Health Agency CKM and the Apperta CKM for UK clinical models are some examples.
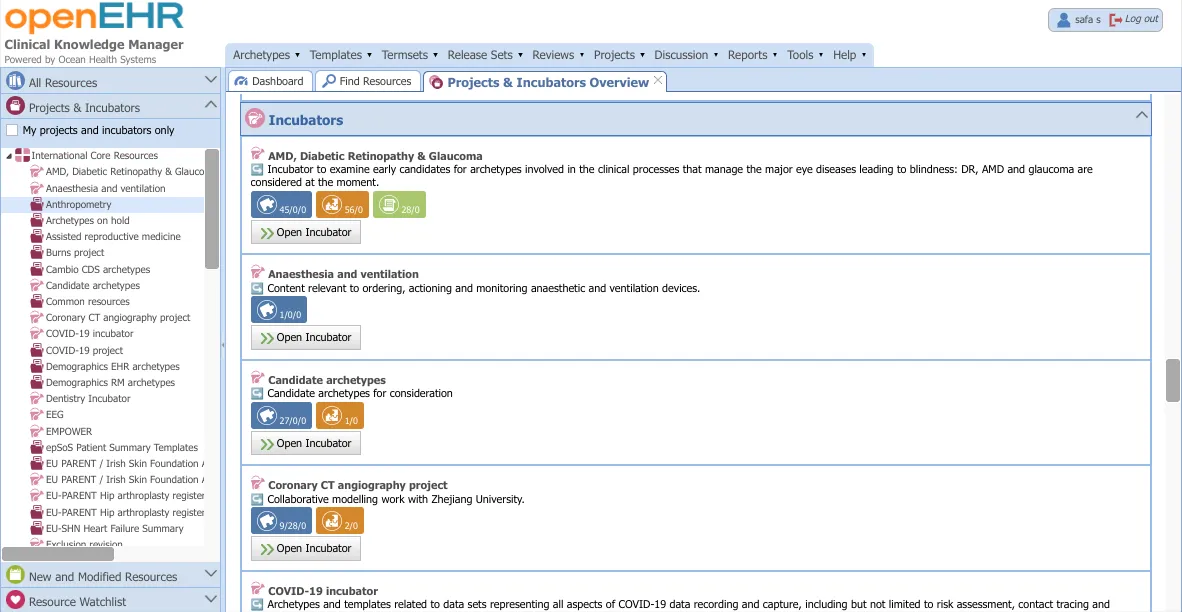
Domains, Projects, Subdomains and Incubators
Each stand-alone instance of the CKM operates as a single domain. It comprises the entire library or repository of primary (archetypes, templates and terminology subsets) and secondary assets (automatically generated).
Each domain has a governed and ungoverned environment that varies in terms of how changes and activities are tracked. The governed content has two levels of structure - subdomains and projects, whereas the ungoverned content is in incubators.
In each domain/instance, there are several subdomains. A subdomain is essentially a logical or practical grouping of projects, each containing archetypes, templates and termsets. Clinical Knowledge Administrators can set up one or more subdomains similar to creating folders. Additionally, a remote subdomain is a subdomain allowing a read-only view of archetypes from a remote CKM instance.
Projects contain strictly governed resources and are used to facilitate formal collaboration, publication, distribution and maintenance of CKM primary assets. This is for a specific clinical purpose or scenario and operates under a subdomain. Each project comprises a collection of one or more models and a project team. E.g. creating a Discharge Summary document, lab report message, data entry screen etc.
Ungoverned spaces in a CKM instance operate as a ‘sandpit’ or asset nursery to foster collaboration, innovation and new asset development. Incubators are such spaces, and can be initiated by any registered user who then becomes the Incubator owner. They can upload new assets into this space. When the assets in an incubator are considered sufficiently mature, the owner can notify the Domain CKAs for permission to transfer this to the main Domain, under a Project.
How is the CKM community structured?
-
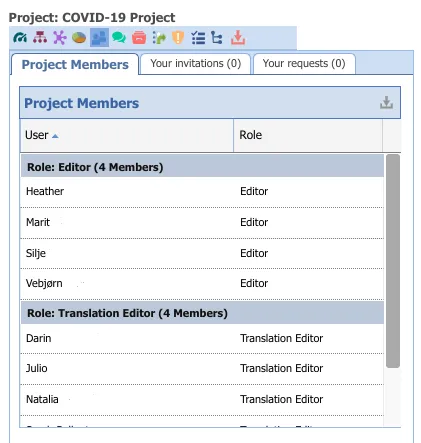
Clinical Knowledge Administrators (CKAs) There are 2-3 CKAs for each CKM, who are responsible for all content management and governance and ensure quality and integrity of clinical artefacts. They are usually highly skilled at archetype design and clinical knowledge governance.CKAs also manage teams and user roles within the community
-
Editors There are usually 5-10 Editors in a CKM, and they work closely with the CKAs. Editors play a leadership role in the development and evolution of clinical models, facilitating review rounds. They also determine precise technical representation of clinical data, ensure appropriate terminology bindings and accurate translations of models.
Project members -
Reviewers Reviewers participate in archetype reviews, and the whole community of registered users can potentially serve as reviewers.
-
Translators, Translation Editors, Translation Reviewers Translators volunteer translations for each archetype, Translation Editors are responsible for running archetype translation reviews, and Translation Reviewers participate in translation reviews.
-
Members Members contribute to the collaborative development and verification of clinical artefacts through participating in reviews. They can also submit candidate translations and join discussion forums.
Final thoughts
The openEHR Clinical Knowledge Manager is a global online repository of clinical data models, particularly archetypes and templates. It is developed and maintained by an active community of clinicians, developers and informaticians and its contents are available open source for reuse by healthcare organizations worldwide.
It serves several key functions in enabling and implementing the core philosophies that drive openEHR, through ensuring standardization and interoperability, supporting collaboration in clinical modelling, and enforcing governance and quality control. Thus the openEHR CKM facilitates reusability and scalability, allowing organizations and countries to reuse archetypes and customize templates without compromising on interoperability.
Like many other open source projects, the openEHR CKM has a long history of collaboratively implemented features and improvements. Over time, the governance and versioning processes have become more robust, incorporating multi-stage and consensus driven approval processes. Domains, Subdomains, Projects, Incubators and Instances allow the development of both specialized and general clinical artefacts according to specific user needs. With a 3000+ strong community, the CKM forms an important part of the openEHR ecosystem, built and maintained in the spirit of collaborative development.
Understanding openEHR and its ecosystem of tools is invaluable for designing future-proof healthcare data systems. Our free openEHR Fundamentals Course can help you understand how to get started, register now!

