
What is a FHIR Terminology Service?
The FHIR terminology service offers functions derived from a collection of CodeSystem, ValueSet, and ConceptMap resources.

Everything about health information standards like openEHR, FHIR, SNOMED CT, LOINC and more.

The FHIR terminology service offers functions derived from a collection of CodeSystem, ValueSet, and ConceptMap resources.


Explore Clayton M. Christensen's vision for healthcare in "The Innovator's Prescription" – a groundbreaking approach to improving patient care.

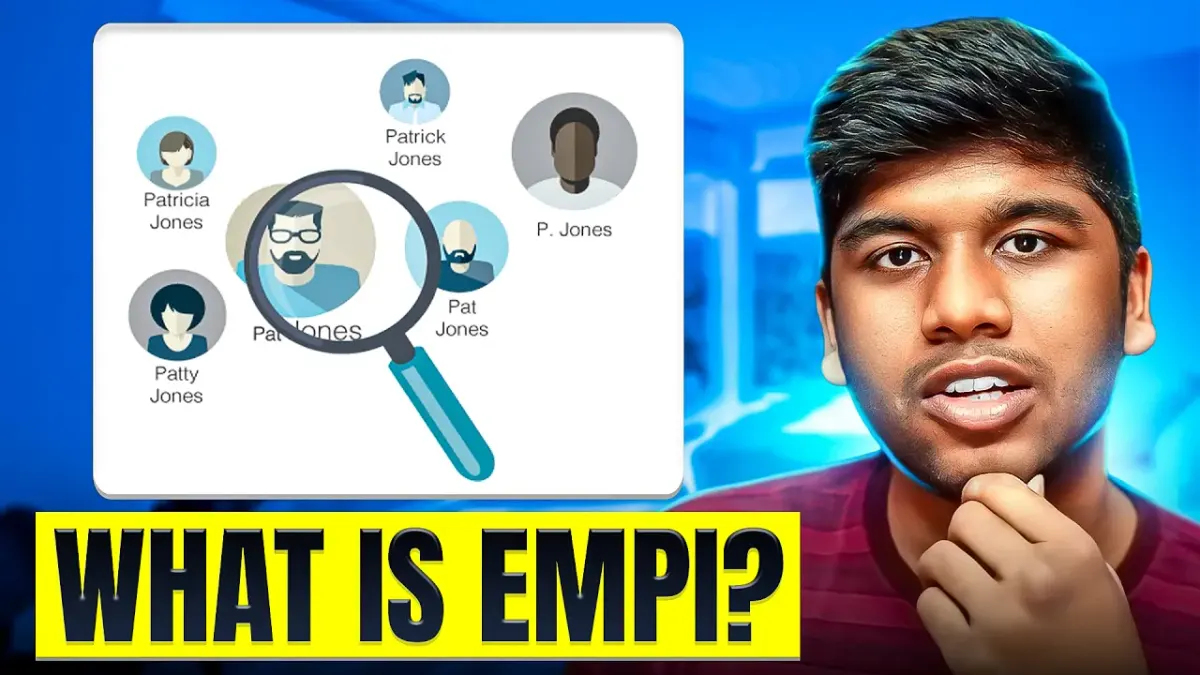
Discover the critical role of Enterprise Master Patient Indexes (EMPI) in managing patient data across healthcare systems, ensuring accuracy and safety in treatment.

Learn to create FHIR patient resources: Navigate HL7, use JSON schemas and code with VS Code for seamless development. Learn healthcare interoperability step-by-step.


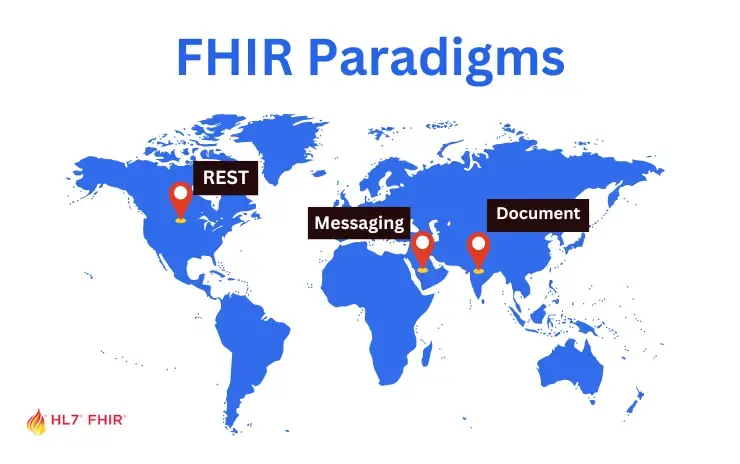
FHIR boosts healthcare data exchange, linking clinical, admin, and research via EHR, REST, Documents, Messages, and Services.

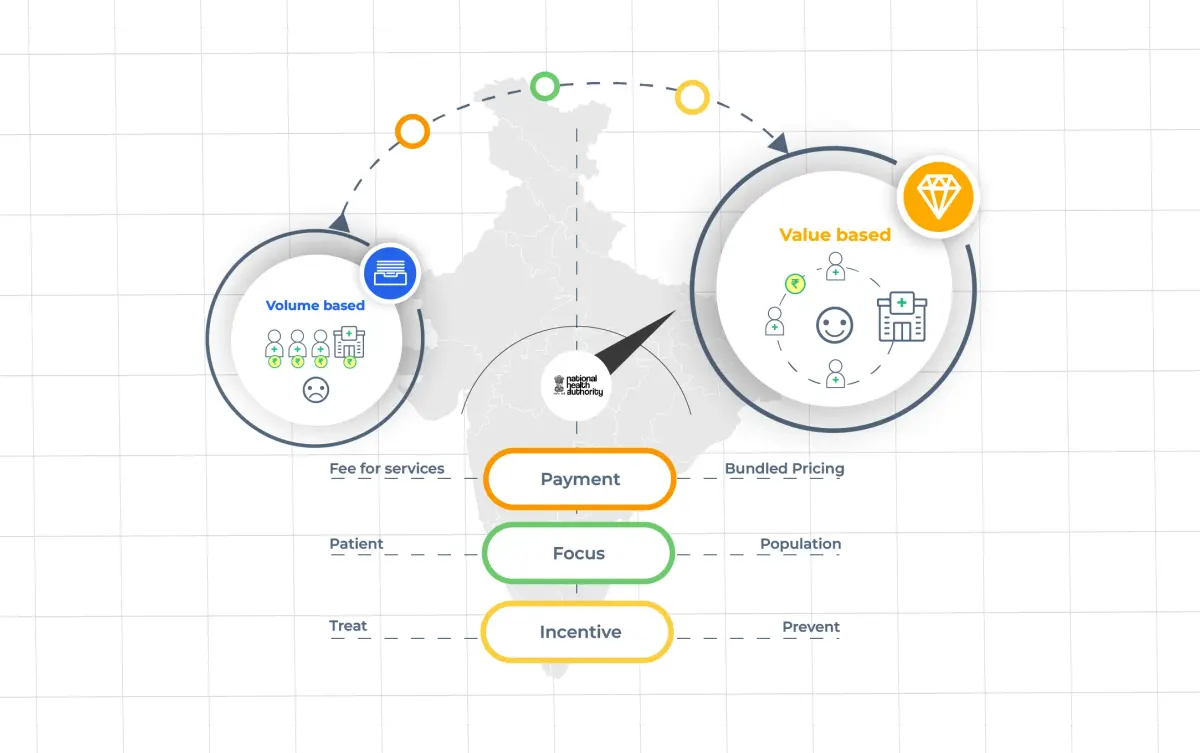
India's PM-JAY aims for value-based care with bundled pricing, tech access, and quality incentives for better health outcomes.

ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) moves data from legacy systems to FHIR, using Apache Debezium and Nifi for syncing databases in FHIR format.


Medblocks digitizes India's healthcare, integrating EHRs with Ayushman Bharat, targeting skill gaps and advancing structured data.
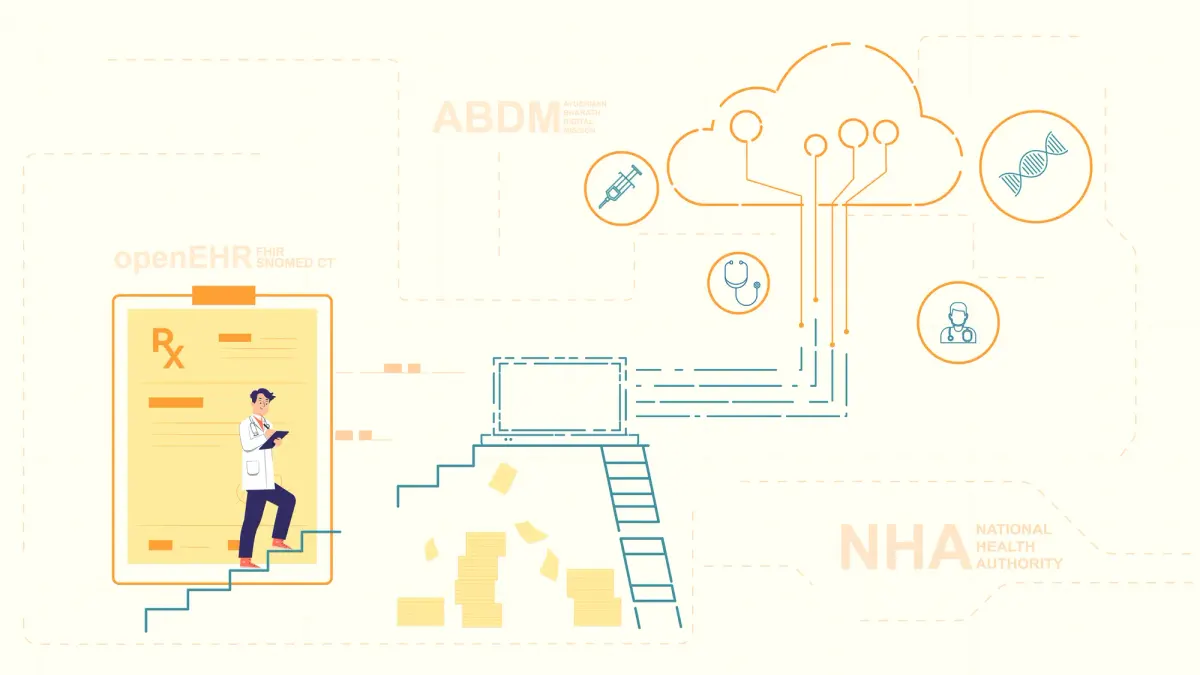

Medblocks implemented all 3 ABDM milestones for Andhra Pradesh's Health Ministry, overcoming challenges with ABHA API, webhook handling, encryption, and FHIR data transformation, contributing to India's digital healthcare evolution.


ABDM digitalizes India's healthcare with health IDs, interoperability, and data security, aiming for universal coverage via digital platforms.


openEHR standardizes health data with archetypes and templates for interoperability. Templates are built from Archetypes using the Archetype Designer Tool.

A beginner friendly guide to to navigating the openEHR CKM or Clinical Knowledge Manager, including searching, viewing and downloading clinical artefacts like archetypes and templates.
